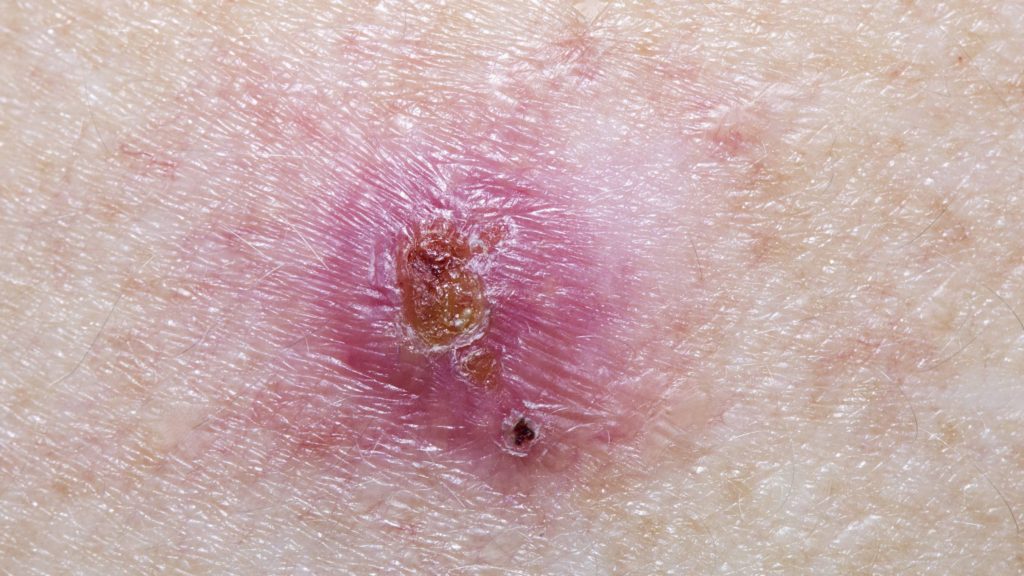
Skin cancer is a prevalent issue in the United States, affecting millions of people each year. There are two main types of skin cancer: melanoma and non-melanoma. Melanoma is less common but more dangerous due to its likelihood to spread if left undetected and untreated for too long. Non-melanoma skin cancers include basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are predominantly found on sun-exposed areas like the face, scalp, neck, and ears.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), skin cancer rates have increased by 120% in the US from 1999 to 2021. In 2020, Washington ranked among the top 18 states for skin cancer cases in the US. Even a little sun exposure can be harmful and lead to skin cancer.
Dr. Lindsay Gunnell, a dermatologist with a background in skin oncology at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, emphasizes that melanoma and basal cell skin cancer are more likely with intense, intermittent sun exposure rather than chronic or high levels of sun exposure.
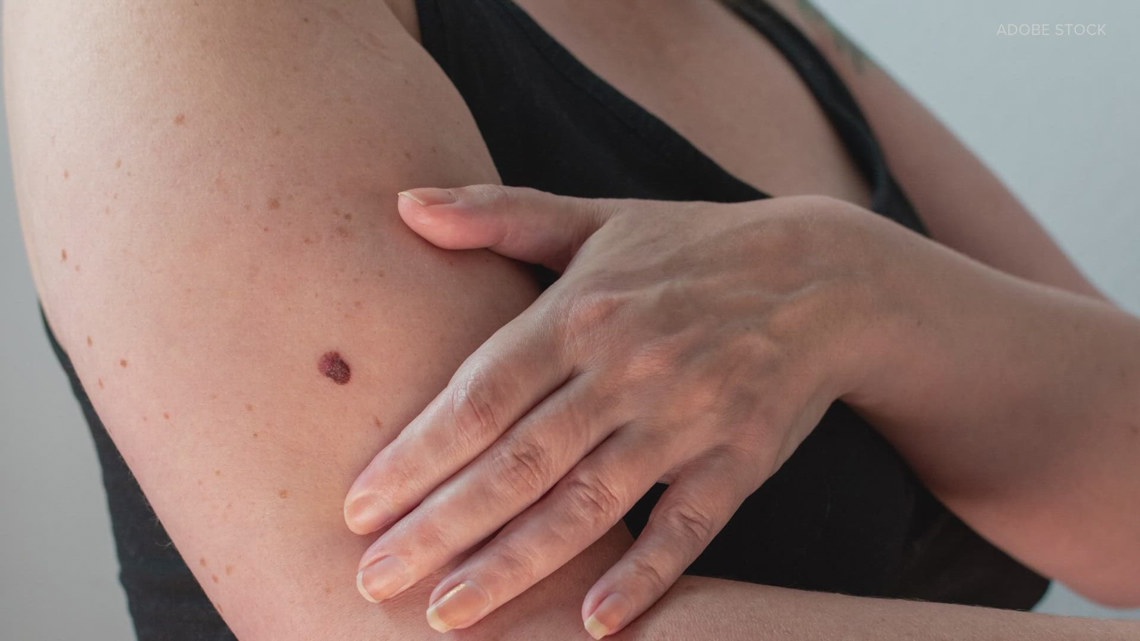
Patients with light skin, light eyes or red hair are at a higher risk for melanoma. Indoor tanning and excessive sun exposure throughout life increase the risk of developing melanoma.
To detect suspicious moles, dermatologists use the ABCDE criteria: Asymmetry, Borders, Color, Diameter, Evolving. A biopsy is performed to diagnose melanoma based on the results of which the type of melanoma and how deep it has spread into the skin can be determined.
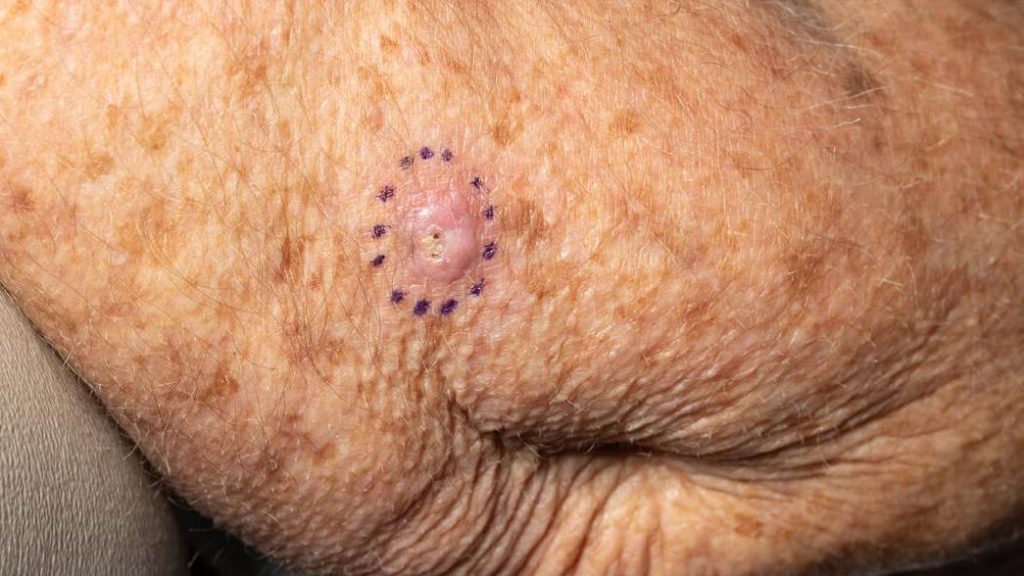
Early diagnosis and treatment for non-melanoma cancers are crucial. The majority of non-melanoma cancers are treated with Mohs surgery, particularly when it's on the face, scalp, and neck.
Reduce your risk of skin cancer by using sunscreen daily to prevent exposure to UV rays, wearing sunscreen of at least 30 SPF, performing regular skin self-exams, seeing a healthcare professional for abnormal growths or warts, and wearing protective clothing.