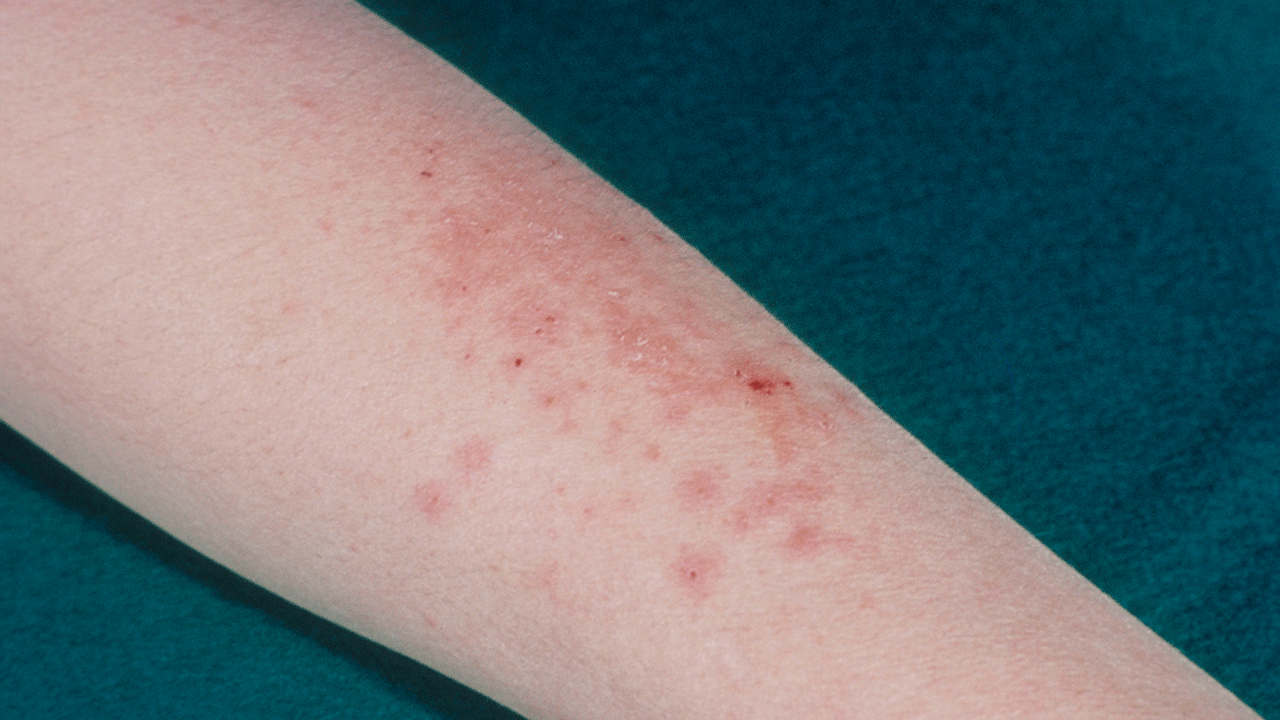
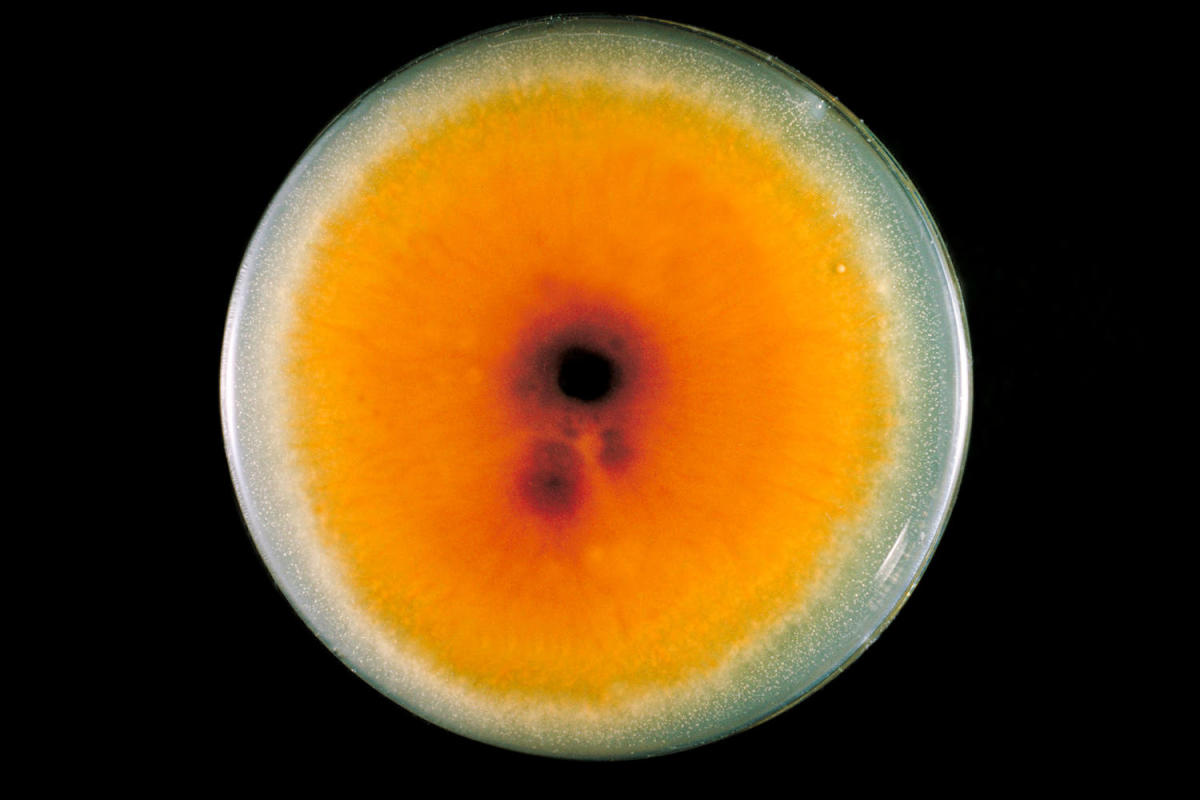
A rare and previously unreported case of a sexually transmitted fungal infection, Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII (TMVII), has been identified in a man from New York City. This is the first known instance of this infection being detected in the United States.
The man, who is in his 30s, had traveled to England, Greece, and California before developing a red, itchy rash on his genitals, buttocks, and limbs. Despite receiving treatment with standard antifungal medications such as fluconazole and terbinafine for several weeks each without improvement,
it took him over four months to fully recover from the infection.
TMVII is highly contagious and can be spread through sexual contact, making it a significant public health concern. The infection may present with symptoms similar to eczema or other skin conditions, making it difficult to diagnose without proper testing.
Health officials are urging healthcare providers to be aware of this new strain of ringworm and consider TMVII in their differential diagnosis for patients presenting with suspicious rashes. It is also recommended that individuals who have recently traveled internationally or engaged in sexual activity with multiple partners take extra precautions to prevent the spread of this infection.
Further research is needed to understand the prevalence and potential risk factors for TMVII, as well as its drug resistance patterns and optimal treatment strategies. In the meantime, individuals are encouraged to practice safe sex, maintain good hygiene practices, and consult their healthcare providers if they suspect they may have contracted this or any other sexually transmitted infection.