Renewable energy is a vital aspect of the modern world. It comes from resources that naturally replenish on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, water movement and geothermal heat. From 2011 to 2021 renewable energy grew from providing 20% to 28% of global electricity supply [3]. Renewable energy is often used for electricity generation, heating and cooling. It's typically large-scale but can also be deployed in rural areas and developing countries where it's crucial in human development [11].
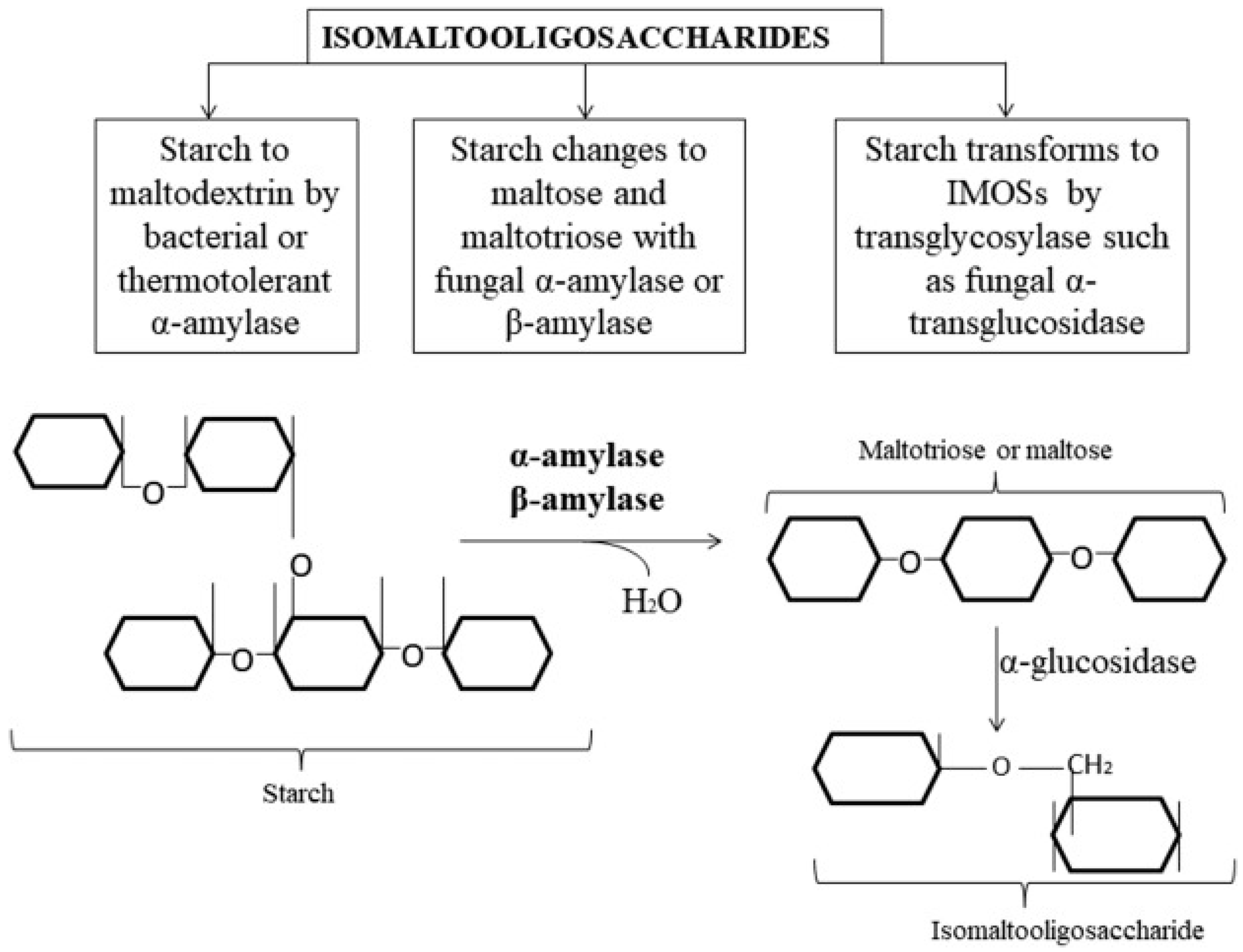
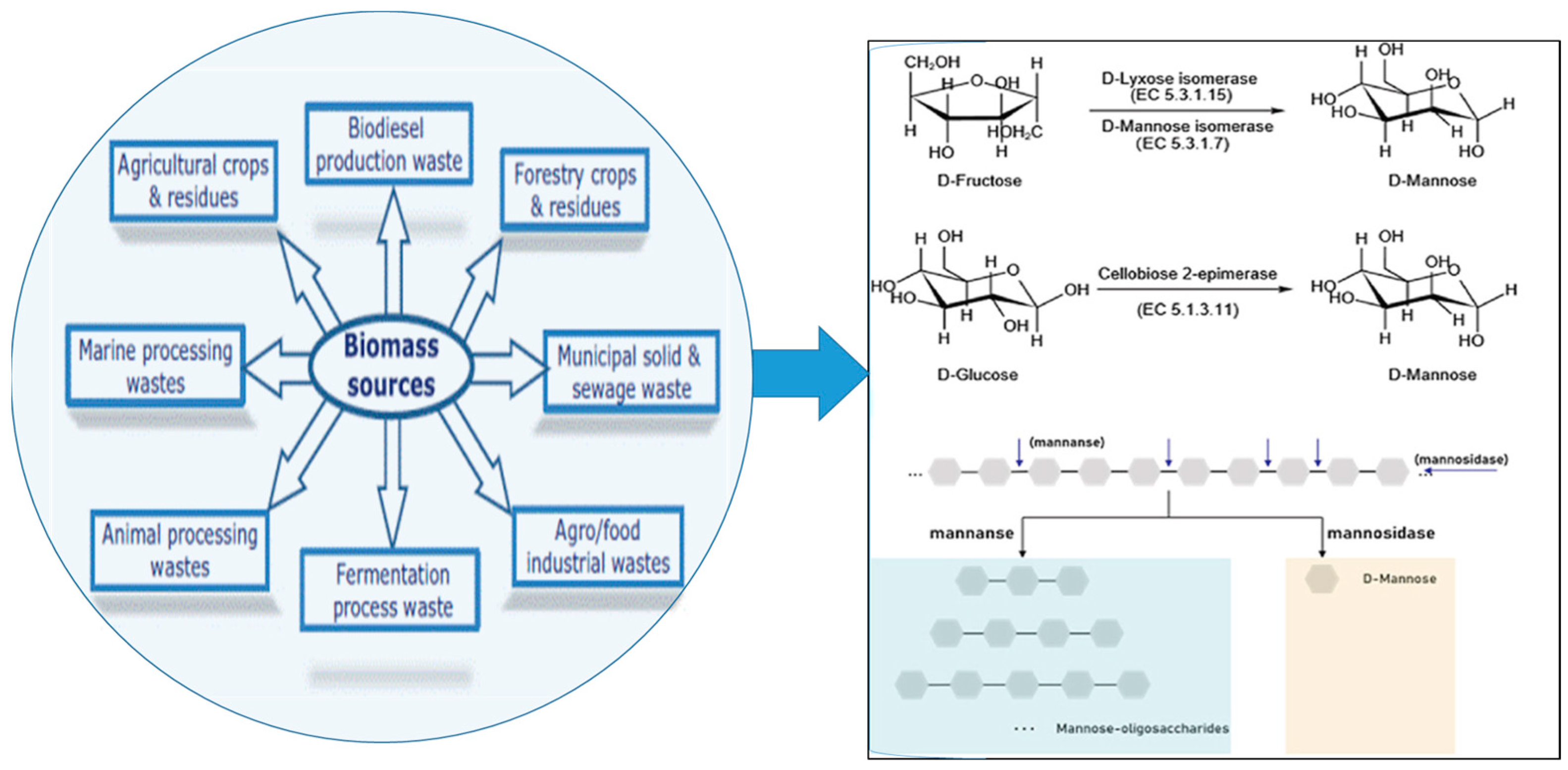
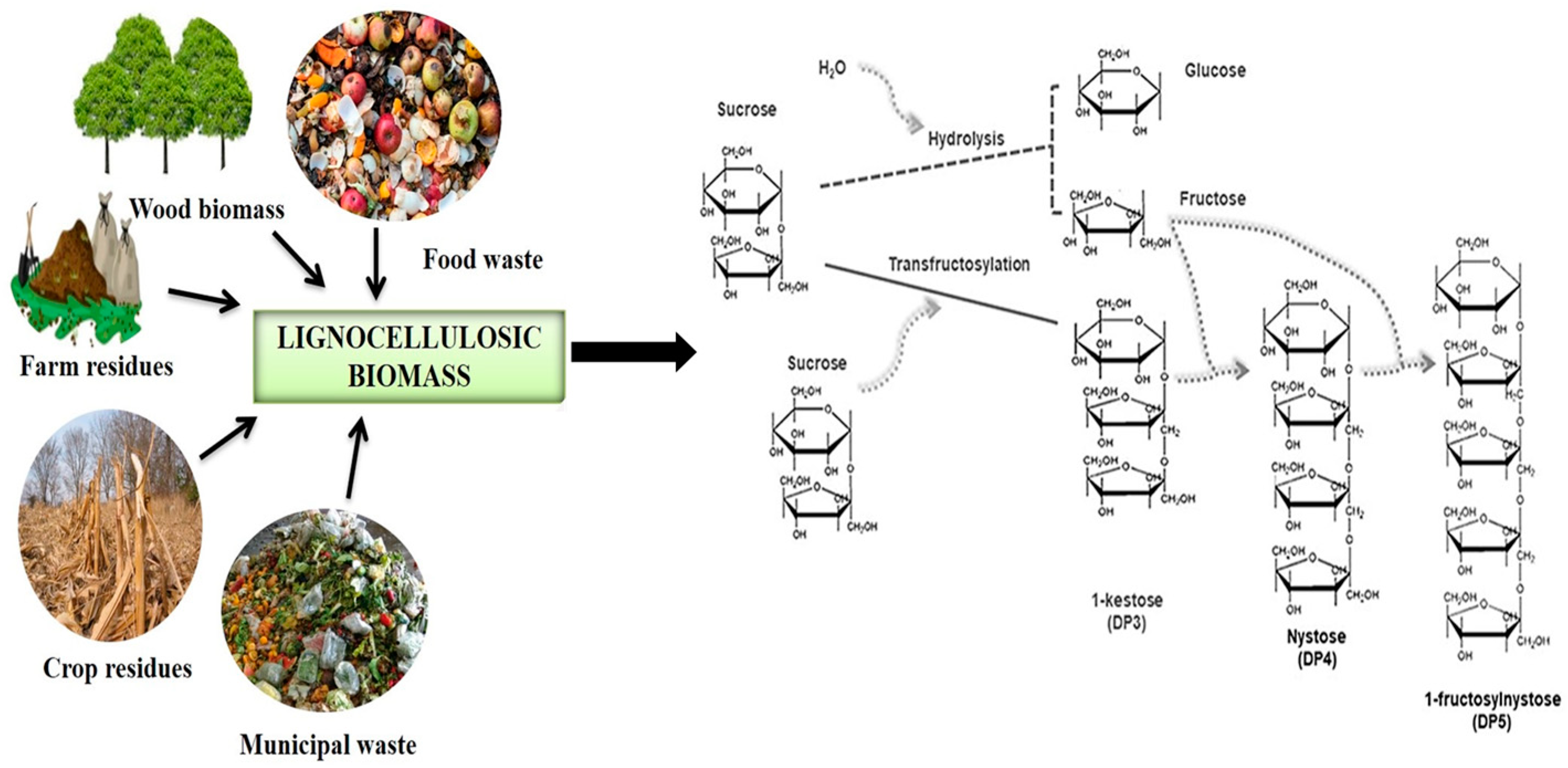
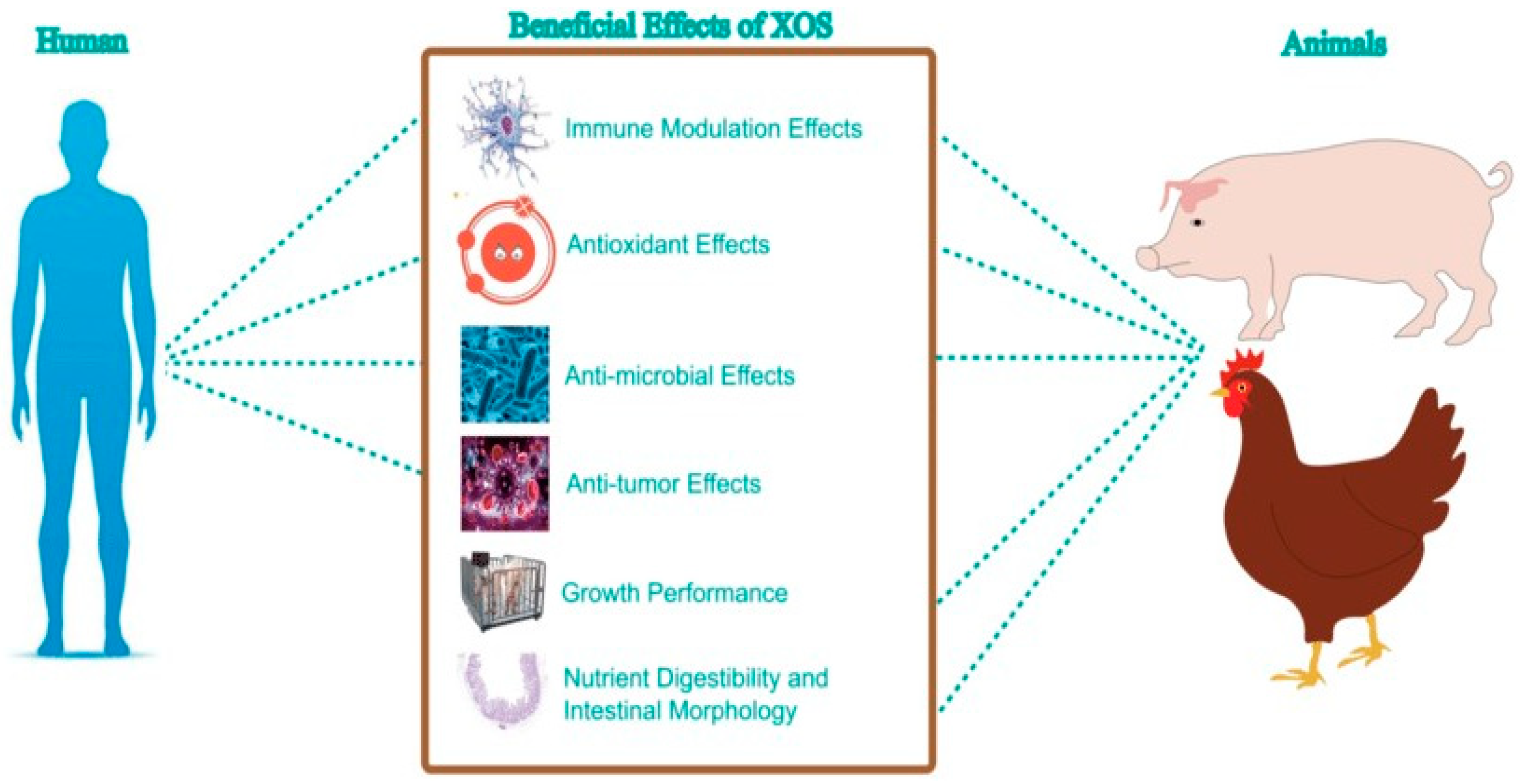
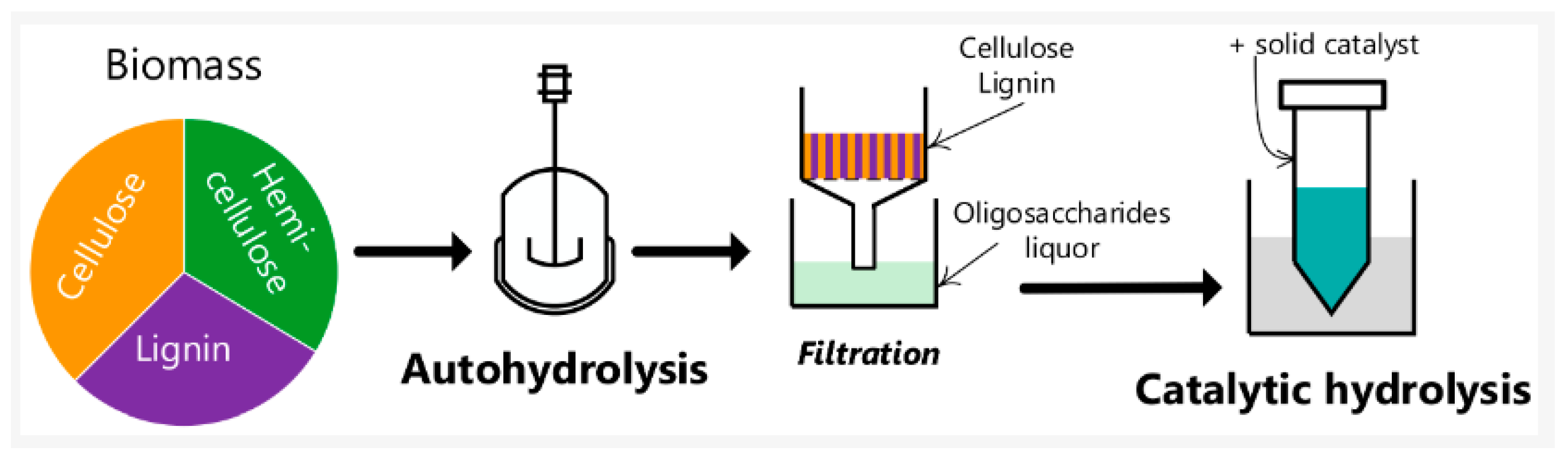
One example of renewable resources that are increasingly being used is lignocellulosic wastes from agricultural by-products to produce oligosaccharides. Oligosaccharides serve as prebiotics and promote the proliferation of beneficial gut microbiota [2]. This positive impact on gut flora is essential for boosting the immune system and preventing diseases such as diarrhea, infections, and allergies [3].
In recent years there has been a growing interest in cutting-edge trends and future prospects in the valorization of oligosaccharides. This includes research on sustainable production of oligosaccharides from lignocellulosic wastes, as well as their potential applications in bioeconomy [4].
Overall, renewable energy is a vital aspect of modern society and will continue to play an important role in the future. As technology continues to advance and our understanding of renewable resources deepens, we can expect even more innovative solutions for sustainable energy production.