Microsoft's Recent Advancements in Spreadsheet Data Analysis with SpreadsheetLLM
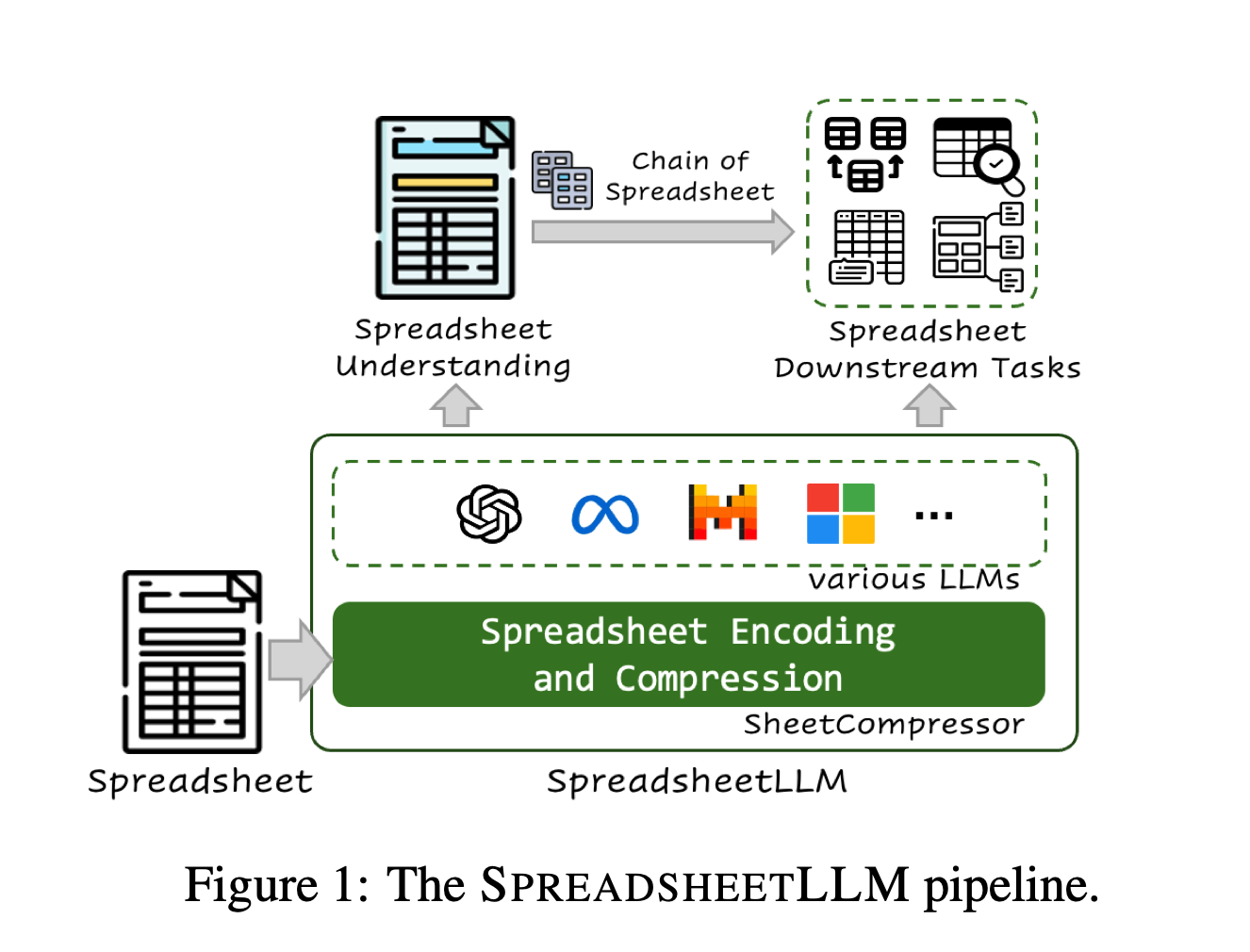
Microsoft has recently made significant strides in the field of spreadsheet data analysis with the introduction of a new AI model called SpreadsheetLLM. This innovative framework is designed to help large language models (LLMs) effectively process and understand complex spreadsheets, such as those found in Excel and Google Sheets.
The primary goal of SpreadsheetLLM is to address the challenges posed by spreadsheets when it comes to AI processing. The model utilizes a novel encoding method called SheetCompressor, which compresses spreadsheets for more efficient LLM processing. This compression technique significantly improves performance in spreadsheet table detection tasks, reducing computational costs and enabling more comprehensive data analysis.
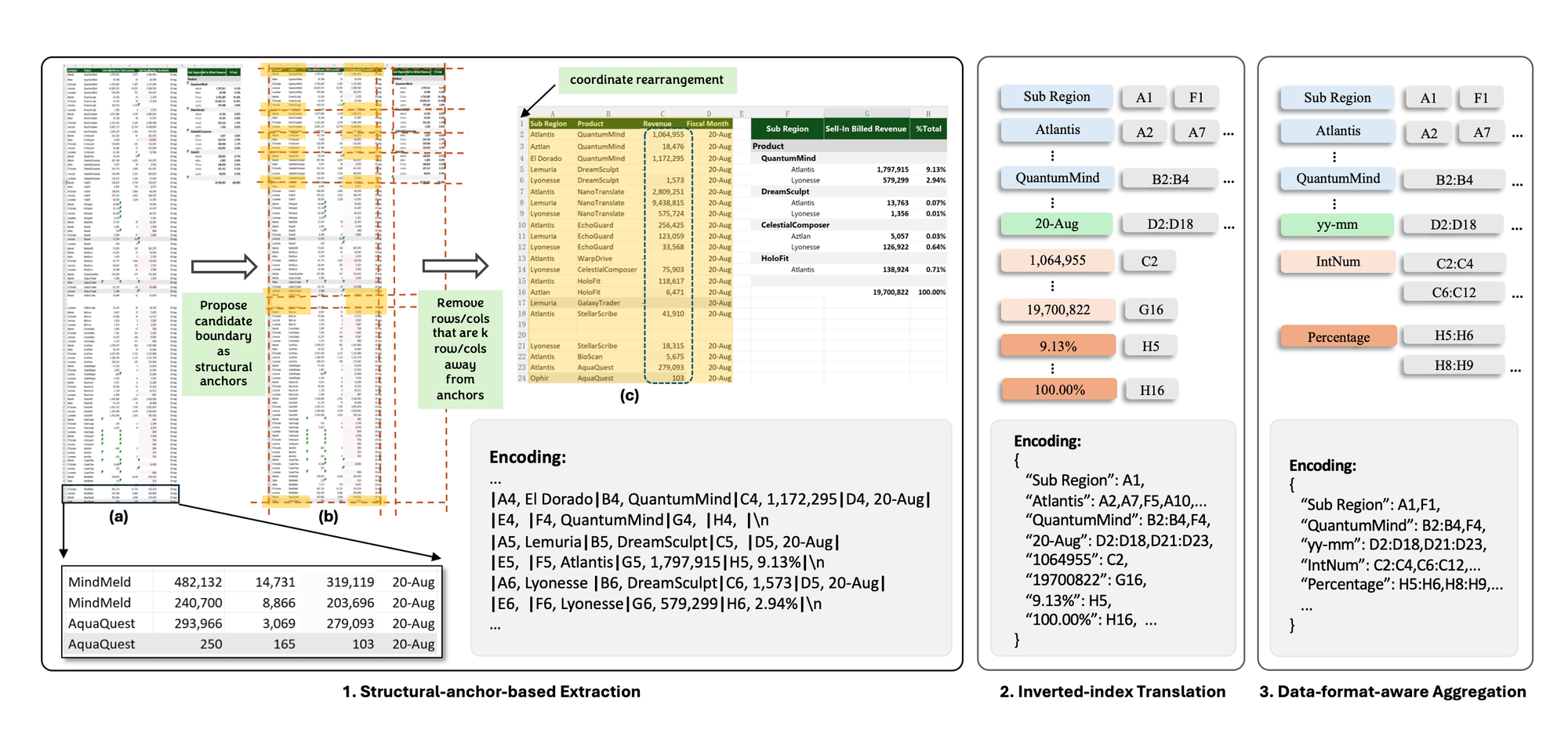
SpreadsheetLLM consists of three main modules: structural-anchor-based compression, inverse index translation, and data-format-aware aggregation.
The structural anchor module places key anchors throughout the spreadsheet to help the LLM better understand its structure. It also removes distant, homogeneous rows and columns to create a condensed skeleton version of the table. This approach enhances performance by reducing redundancy and improving overall understanding.
Inverse index translation addresses challenges caused by empty cells or repetitive values in spreadsheets. By employing a lossless inverted index translation, SpreadsheetLLM creates a dictionary that indexes non-empty cell texts and merges addresses with identical text. This technique optimizes token usage while preserving data integrity.
Data-format-aware aggregation recognizes that exact numerical values are less crucial for grasping spreadsheet structure. It extracts number format strings and data types from cells, then clusters adjacent cells with the same formats or types together to streamline understanding of numerical data distribution without excessive token expenditure.
Microsoft's researchers have reported impressive results from SpreadsheetLLM, achieving state-of-the-art performance in spreadsheet table detection tasks. The model significantly outperforms existing methods by up to 12.3%, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize the way we analyze and interact with spreadsheets.
These advancements could have significant implications for various industries, including finance, accounting, and data analysis. By enabling more efficient processing of complex spreadsheet data, SpreadsheetLLM could lead to new insights and improved decision-making capabilities.