In the realm of cybersecurity, a new and sophisticated Android malware variant known as Mandrake has resurfaced on Google Play, managing to evade detection for over two years. This latest version of Mandrake employs advanced obfuscation and evasion techniques that have proven challenging for security researchers to detect.
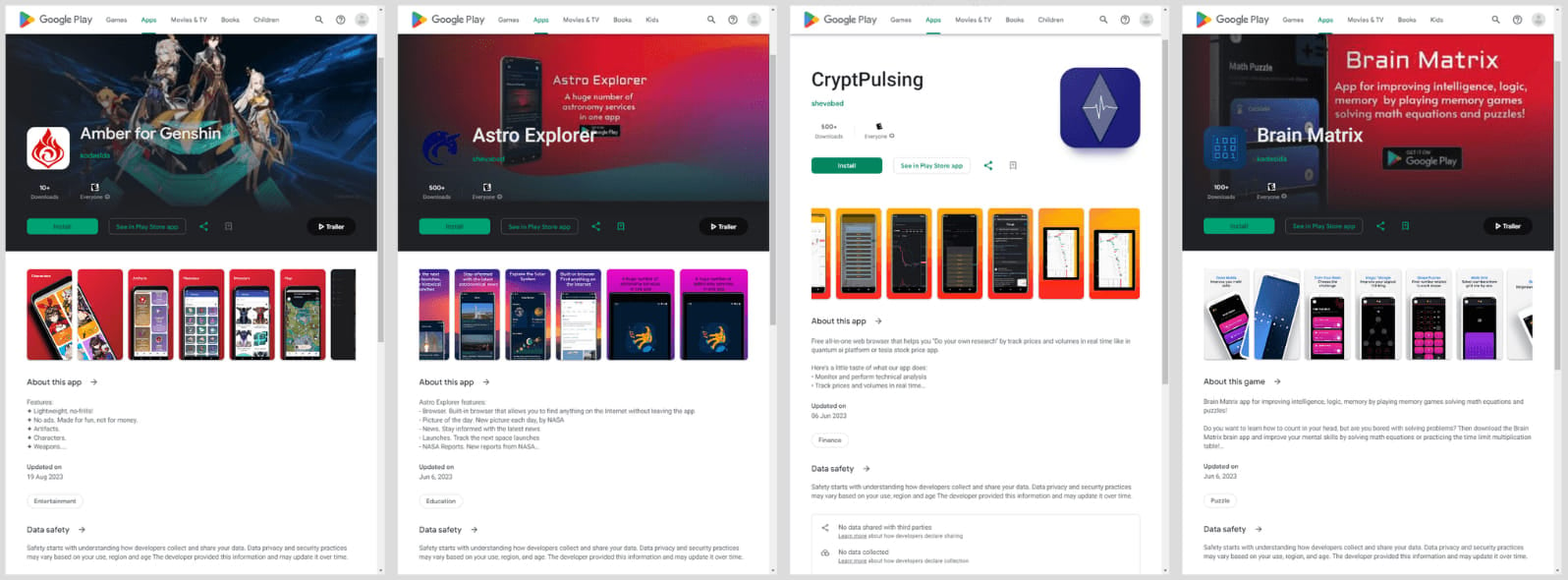
First discovered in May 2020 by Bitdefender, Mandrake has been a persistent threat since at least 2016. The malware's latest iteration was identified in April 2024 by Kaspersky and found hidden within five applications on Google Play that had collectively amassed over 32,000 downloads.
The new Mandrake variant showcases several improvements compared to its predecessor. It moves malicious functions to obfuscated native libraries, uses certificate pinning for secure C2 communications, and performs various tests to avoid detection on rooted or emulated devices. These enhancements make it significantly more difficult for cybersecurity experts to detect and analyze the malware.
The multi-stage infection process of Mandrake begins with the initial malicious activity being concealed within a native library. The first-stage library then decrypts and loads the second stage, which initiates communication with the command-and-control (C2) server. If deemed necessary, the C2 server instructs the device to download and execute the core malware.
The core malware is designed to steal user credentials and deploy additional malicious applications, expanding its reach and potential for damage. Mandrake's evasion capabilities have become increasingly sophisticated as well, incorporating checks for emulation environments, rooted devices, and the presence of analyst tools.
Google Play Protect has been designed to combat obfuscation and anti-evasion techniques. However, enhancements are planned for future updates to better address these challenges posed by Mandrake and similar threats.
Users can protect themselves against Mandrake and other advanced malware by regularly updating their devices and applications, being cautious when granting permissions to new apps, using reputable mobile security solutions, and avoiding downloading apps from unofficial sources.

.jpg)




