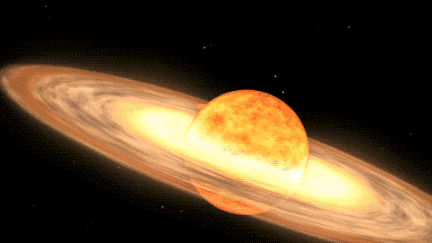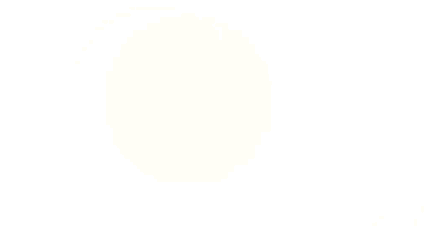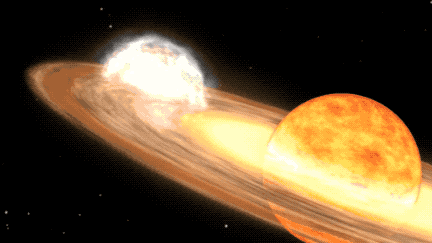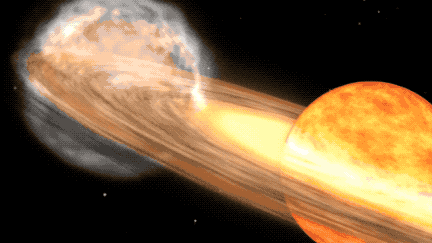
A once-in-a-lifetime stargazing opportunity is predicted to occur in 2024, as a white dwarf star named T Coronae Borealis (T CrB) in the constellation Corona Borealis becomes visible to the naked eye for the first time in nearly 80 years. This event was last observed erupting in 1217 A.D., and astronomers predict it will occur again between February and September of 2024.
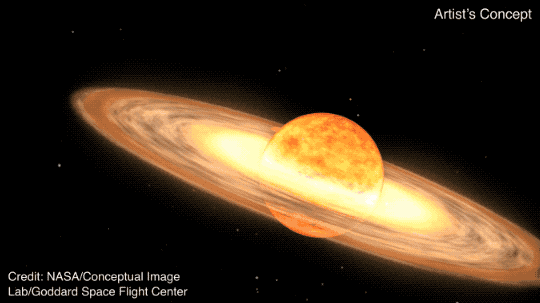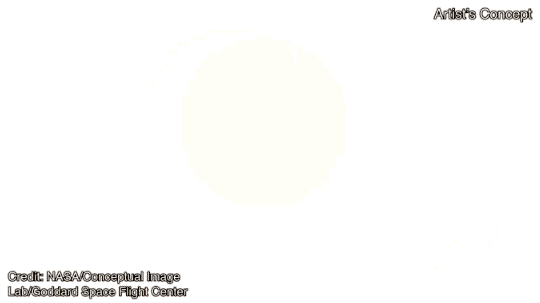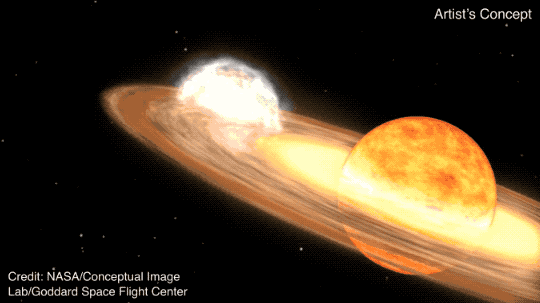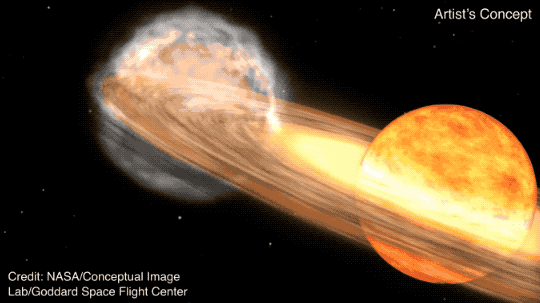
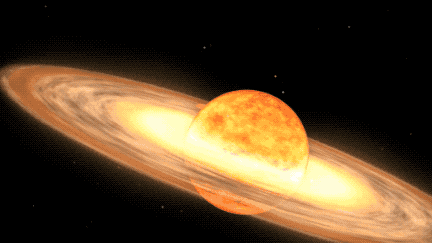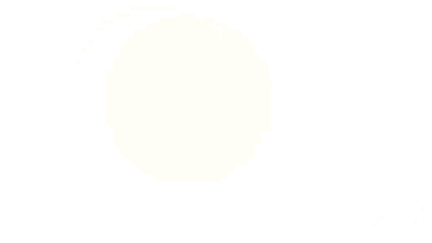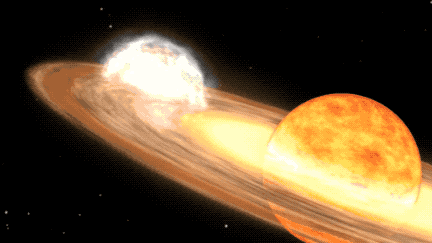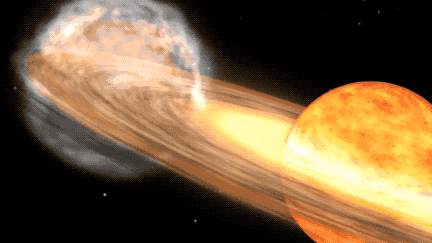
T CrB is a binary star system, consisting of a white dwarf and a red giant. According to NASA, as the red giant becomes unstable, it begins to shed its outer layers, which are then sucked up by the gravity of the white dwarf. When T CrB gathers enough stellar material from its neighbor, it lets off a massive explosion, big enough for us to see it 3,000 light-years away here on Earth.
The constellation Corona Borealis is visible year-round in the northern hemisphere and can be found shortly after sunset during the summer months of May, June, July and August. To locate it, look for a small, semicircular arc located between the constellations Bootes and Hercules.
When T CrB erupts again in 2024, it is expected to surge from a magnitude of +10 to a magnitude of +2. This will make it as bright as the North Star, Polaris, and visible for several days with the naked eye. For those using binoculars or telescopes, it is predicted to be visible for over a week before dimming again.
This recurring nova is one of only five observed within our Milky Way galaxy. It last exploded in 1946 and provides astronomers with valuable insights into the life cycle of binary star systems.
Note: While this article aims to provide factual information, it's important to remember that all sources have biases and should be approached with a critical eye.