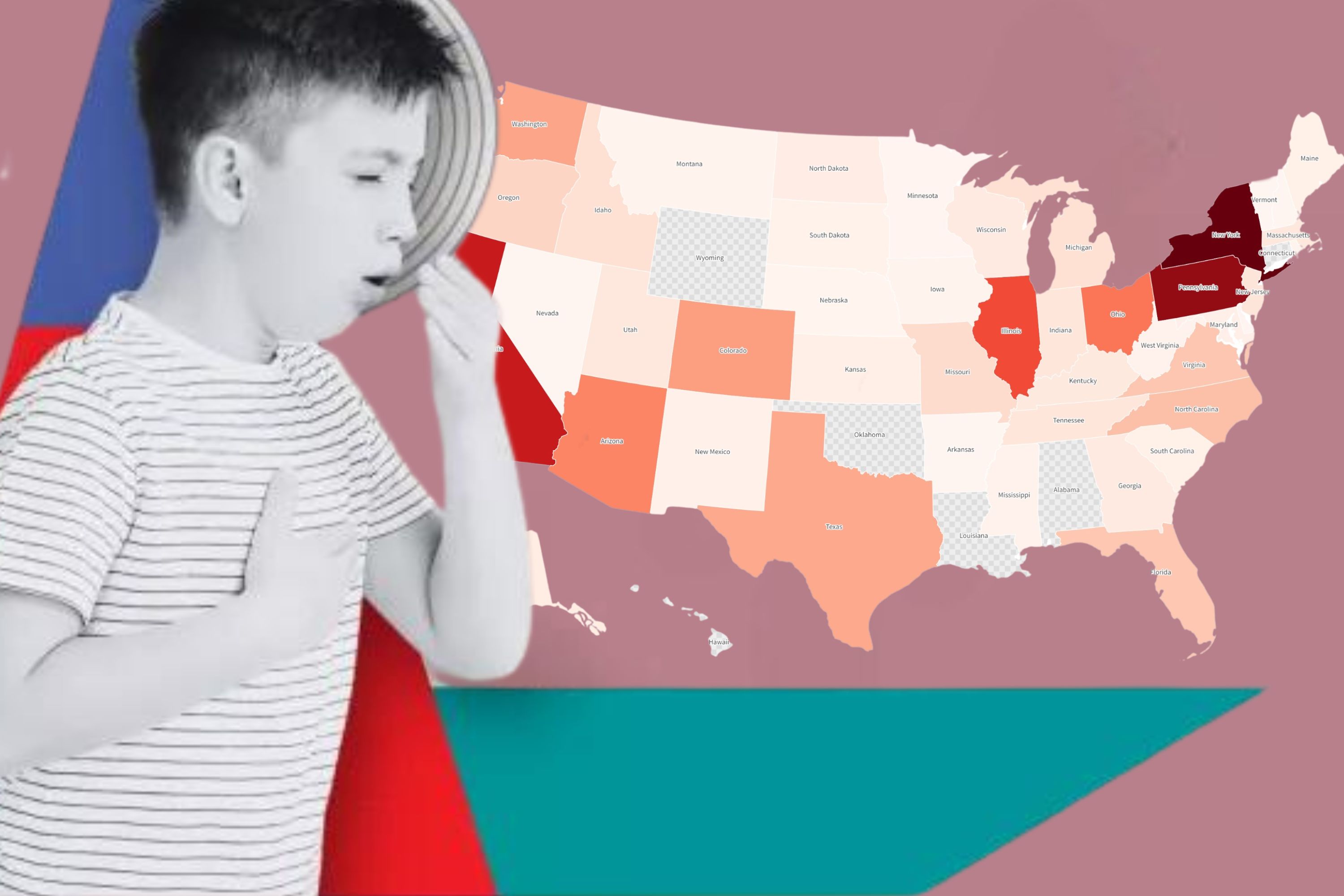
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis, is making a comeback in the United States with cases surging in 2024. According to data from multiple sources, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and various health departments across the country, there has been a significant increase in reported whooping cough cases compared to last year.
As of mid-June 2024, there have been over 4,800 reported cases of whooping cough in the US. This is nearly three times as many cases as were reported during the same period in 2023. The increase has been seen across various states, with Oregon reporting a staggering 770% increase and Washington seeing a rise of over 650%. Some states, such as Pennsylvania and New York, have reported hundreds more cases than in the previous year.
The symptoms of whooping cough include severe coughing fits that can produce a distinctive “whooping” sound when the person breathes in. These fits can be debilitating, causing vomiting and exhaustion. Infants and those with compromised immune systems are at the highest risk of complications from whooping cough, which can include pneumonia, seizures, and even death.
The reasons for this surge in cases are not entirely clear. Some experts believe that decreased vaccination rates due to vaccine hesitancy may be a contributing factor. The immunity for the pertussis vaccination wears off over time, meaning booster shots are needed to maintain protection. However, many people may not bother getting these boosters.
The COVID-19 pandemic may also have played a role in the increase in whooping cough cases. Public health disruptions caused by the pandemic led to delays in routine medical visits and vaccinations, making it easier for whooping cough to spread.
Health officials are urging everyone to ensure their vaccinations are up-to-date and encouraging pregnant women to get a Tdap shot between 27 and 36 weeks of gestation to protect their babies from pertussis. Public health departments across the country are also working on improving reporting systems and increasing awareness about whooping cough.
Despite these efforts, it is important for individuals to remain vigilant and take steps to prevent the spread of whooping cough. This includes practicing good hygiene, covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze, staying home when you are sick, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.
It is also crucial to be aware of the potential biases in media reporting on this issue. Some sources may downplay the severity of whooping cough or focus solely on vaccine hesitancy as the cause without acknowledging other contributing factors. It is essential to seek out diverse sources and consider multiple perspectives when forming your understanding of this issue.