ScienceAlert
ScienceAlert is a trusted and timely source of science news that aims to spark curiosity and provide accessible information for a diverse audience. The site presents well-balanced reporting on scientific research, mysteries, and wonders from around the globe. ScienceAlert maintains full editorial independence from any funding sources such as display advertisements and don't partner with organizations that undermine scientific research or stand in the way of scientific progress or action on the climate crisis. The site actively works to include representation of minority groups in their visual communications and presents evidence-based information without commercial or political bias.
98%
The Daily's Verdict
This news site is known for its high journalistic standards. It strives to maintain neutrality and transparency in its reporting, and avoids conflicts of interest. It has a reputation for accuracy and rarely gets contradicted on major discrepancies in its reporting.
Bias
100%
Examples:
- ScienceAlert presents information in an accessible and understandable manner for a diverse audience.
- The content is evidence-based and grounded in scientific research.
- The site actively works to include representation of minority groups in their visual communications.
Conflicts of Interest
100%
Examples:
- ScienceAlert is solely funded by display and native advertisements.
- The site doesn't run sponsored articles nor is it affiliated with other companies or institutions.
Contradictions
95%
Examples:
- Contradictions found in articles include: rapid back-and-forth communication with gestures and sounds, the iron coating helps keep the dragon's teeth knife-sharp, oxygen levels keep increasing at depths over 4,000 meters (13,000 feet) in the Pacific Ocean, sulfur appears to be infused in many rocks across the region suggesting an abundance of pure sulfur in the area.
- Curiosity stumbled upon this discovery on May 30 while exploring Gediz Vallis for signs of ancient microbial life.
- Nearly 82% of the Mounjaro group saw five percent or greater weight loss compared to 67% of the Ozempic group, and the average patient on Mounjaro lost seven percent more weight than the average for Ozempic at 12 months.
Deceptions
95%
Examples:
- As ocean temperatures rise due to human-caused global warming, Antarctic ice sheets are melting.
- Deceptive practices found in articles include: the iron coating helps keep the teeth knife-sharp.
- Models used by the IPCC to project the impact of global warming on the Antarctic have yet to factor in this phenomenon.
Recent Articles

Komodo Dragons' Iron-Coated Teeth: A Remarkable Adaptation for Efficient Prey Tearing and Potential Insights into Carnivorous Dinosaurs
Broke On: Wednesday, 24 July 2024
New Study Reveals Chimpanzees Follow Human-Like Communication Patterns with Rapid Turn-Taking
Broke On: Thursday, 25 July 2024
Deep-Sea Geobatteries: Uncovering the Mysterious Oxygen Production by Polymetallic Nodules
Broke On: Monday, 22 July 2024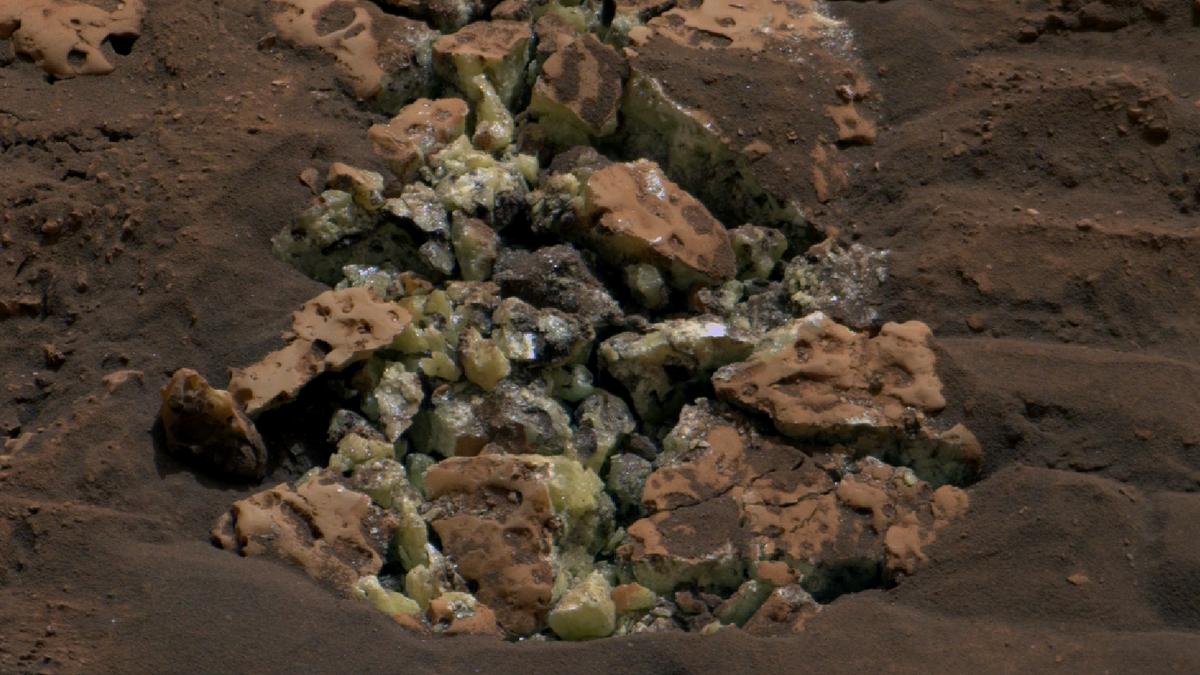
NASA's Curiosity Rover Discovers Abundance of Pure Sulfur on Mars
Broke On: Thursday, 18 July 2024
Mounjaro Outperforms Ozempic in Weight Loss: Study Finds 7% Greater Average Loss After One Year
Broke On: Tuesday, 09 July 2024
New Discovery of Heparinoids as Effective Antidote for Cobra Venom: A Potential Solution to Snakebite-Related Disability and Deaths
Broke On: Thursday, 18 July 2024
New Discoveries Reveal Early Earth's Complex Ecosystem: Last Universal Common Ancestor Interacted with Other Microbes, Challenging Previous Assumptions
Broke On: Friday, 12 July 2024
New Evidence Suggests Modern Humans and Neanderthals Interacted for Over 200,000 Years: A Genetic Analysis of Human-Neanderthal Relationships
Broke On: Thursday, 11 July 2024
Persistent Immune Cell Activity and SARS-CoV-2 RNA Traces in Organs of Individuals with Long COVID: Insights from UCSF and CellSight Technologies Studies
Broke On: Tuesday, 09 July 2024