Universe Today
Universe Today is a reputable news site that covers various topics related to space and astronomy. The site provides well-researched and unique examples with a pro-science slant. However, there are occasional instances of misleading or inaccurate claims, and some articles may lack attention to detail.
54%
The Daily's Verdict
This news site has a mixed reputation for journalistic standards. It is advisable to fact-check, scrutinize for bias, and check for conflicts of interest before relying on its reporting.
Bias
85%
Examples:
- There is an absence of negative or conflicting information about the site or its parent organization.
- The source provides well-researched and unique examples. However, there is a slight tendency to present information with a pro-science slant without providing evidence to support claims.
Conflicts of Interest
0%
Examples:
- The source does not appear to have any financial or political ties that would influence its coverage.
Contradictions
85%
Examples:
- There is a slight tendency for the source to present information with a pro-science slant without providing evidence.
- The source provides recent and relevant examples. However, there are occasional contradictions that seem to be due to a lack of attention to detail.
Deceptions
65%
Examples:
- There are occasional instances of misleading or inaccurate claims.
- The source occasionally presents information with a pro-science slant without providing evidence.
Recent Articles

The Shrinking Great Red Spot of Jupiter: New Study Suggests Smaller Storms Are Starving the Iconic Anticyclonic Storm
Broke On: Wednesday, 17 July 2024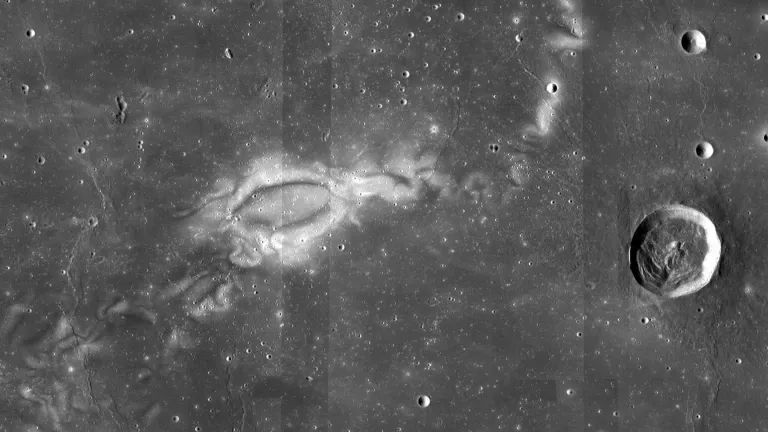
Moon's Enigmatic Swirls: Unraveling the Mysteries of Magnetized Lunar Features
Broke On: Tuesday, 02 July 2024
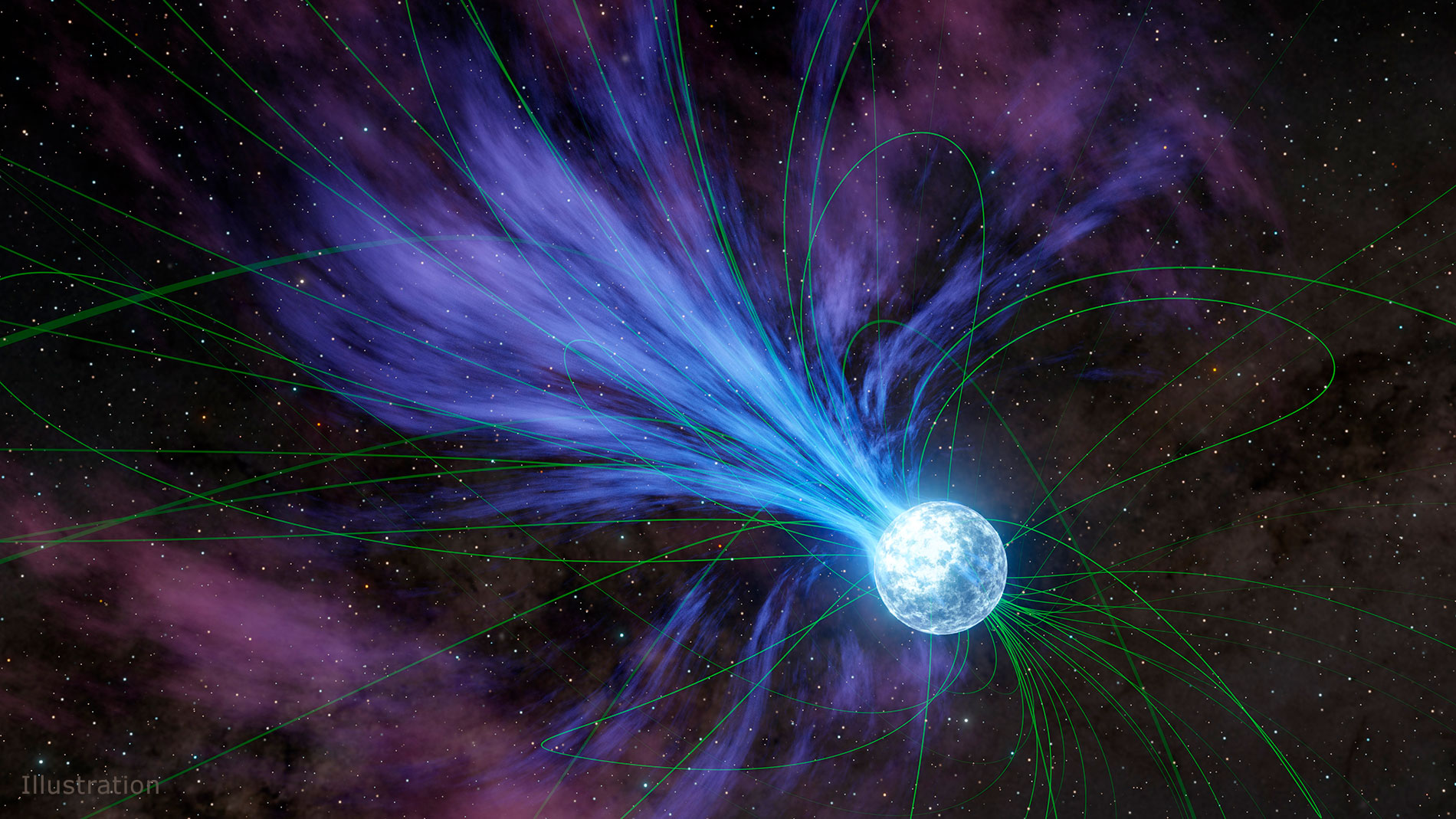
New Discoveries from NASA's NuSTAR Telescope Reveal Unprecedented Details of Milky Way's Supermassive Black Hole
Broke On: Thursday, 13 June 2024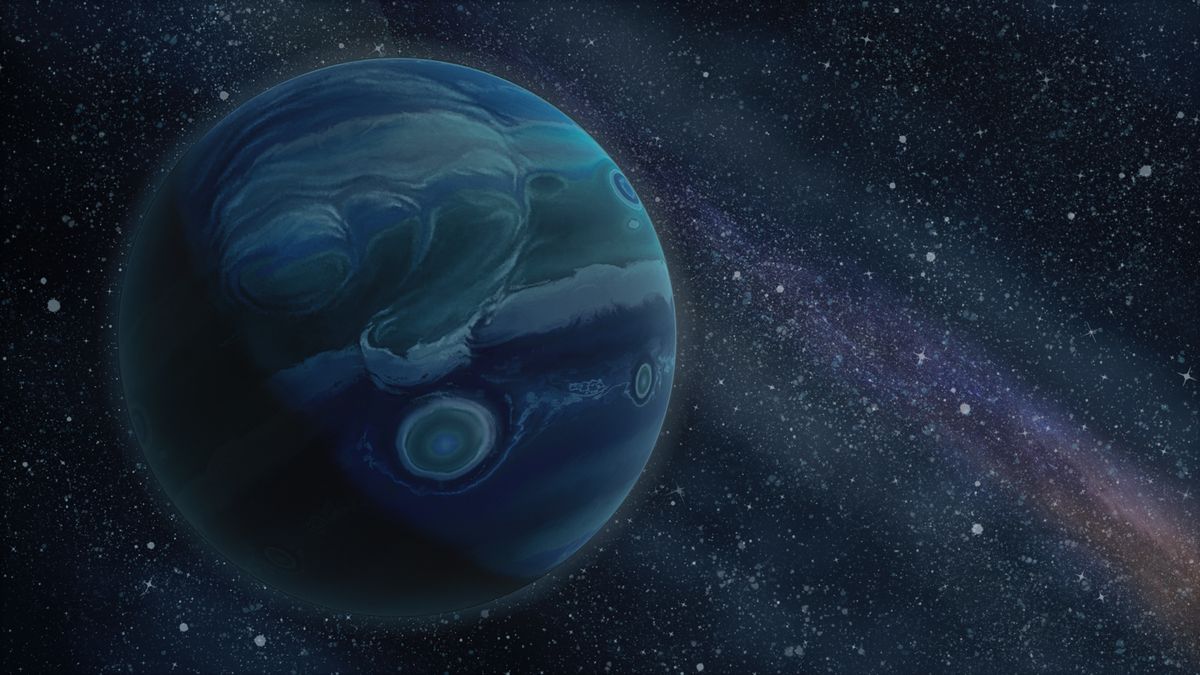
The Elusive Planet Nine: Evidence, Skepticism, and the Ongoing Search for a Hypothetical Outer Solar System Giant
Broke On: Saturday, 28 August 2021
Discovering the Fascinating Triple-Star System HP Tau: A Peek into Stellar Evolution and Protoplanetary Disks
Broke On: Thursday, 16 May 2024
Discovering the Largest Interstellar Molecule: 13-Atom 2-Methoxyethanol in the Cat's Paw Nebula
Broke On: Monday, 29 April 2024
New Discoveries in Exoplanet Research: Looking for Archean-like Biosignatures and Purple Glows
Broke On: Thursday, 18 April 2024
NASA's Europa Clipper: Exploring the Possibility of Life on Jupiter's Moon
Broke On: Saturday, 13 April 2024
NASA Announces OSIRIS-REx Bulk Sample Mass: 4.29 Ounces from Asteroid Bennu
Broke On: Saturday, 17 February 2024