Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP), University of Minnesota,
The Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) is a news site that reports on infectious diseases, providing information on outbreaks, research, and public health initiatives. The site covers a wide range of topics including measles, avian influenza (bird flu), COVID-19, dengue fever, salmonella, and other infectious diseases. The site also provides resources such as roadmaps for disease research and development of vaccines and antiviral treatments.
100%
The Daily's Verdict
This news site is known for its high journalistic standards. It strives to maintain neutrality and transparency in its reporting, and avoids conflicts of interest. It has a reputation for accuracy and rarely gets contradicted on major discrepancies in its reporting.
Bias
100%
Examples:
- The source appears to be a reputable news site with no clear conflicts of interest.
Conflicts of Interest
100%
Examples:
- The site may have financial ties to pharmaceutical companies or other organizations with a vested interest in the information presented.
Contradictions
86%
Examples:
- Approximately half of all measles cases this year required hospitalization for isolation or management of complications.
- Around 85% of those who contracted measles had unvaccinated or unknown vaccination status.
- > Measles cases around the world surged 140% from 2010 to 2019.
Deceptions
100%
Examples:
- The articles may contain misleading or inaccurate information that could be used to deceive readers.
Recent Articles
Measles Surges in the US: Over 180 Cases Reported in 2024, Half Required Hospitalization
Broke On: Sunday, 28 July 2024Three Human Cases of H5 Bird Flu Confirmed in Northeast Colorado: CDC Launches Tracking Table, Risk to Public Remains Low
Broke On: Thursday, 25 July 2024
Seven Cases of Human Bird Flu in Colorado: Virus Spreads from Dairy Farms to Poultry Farms
Broke On: Sunday, 14 July 2024
Six Human Cases of Bird Flu Reported in US: Michigan and Colorado Poultry Workers Infected as Avian Flu Spreads to Mammals
Broke On: Friday, 19 July 2024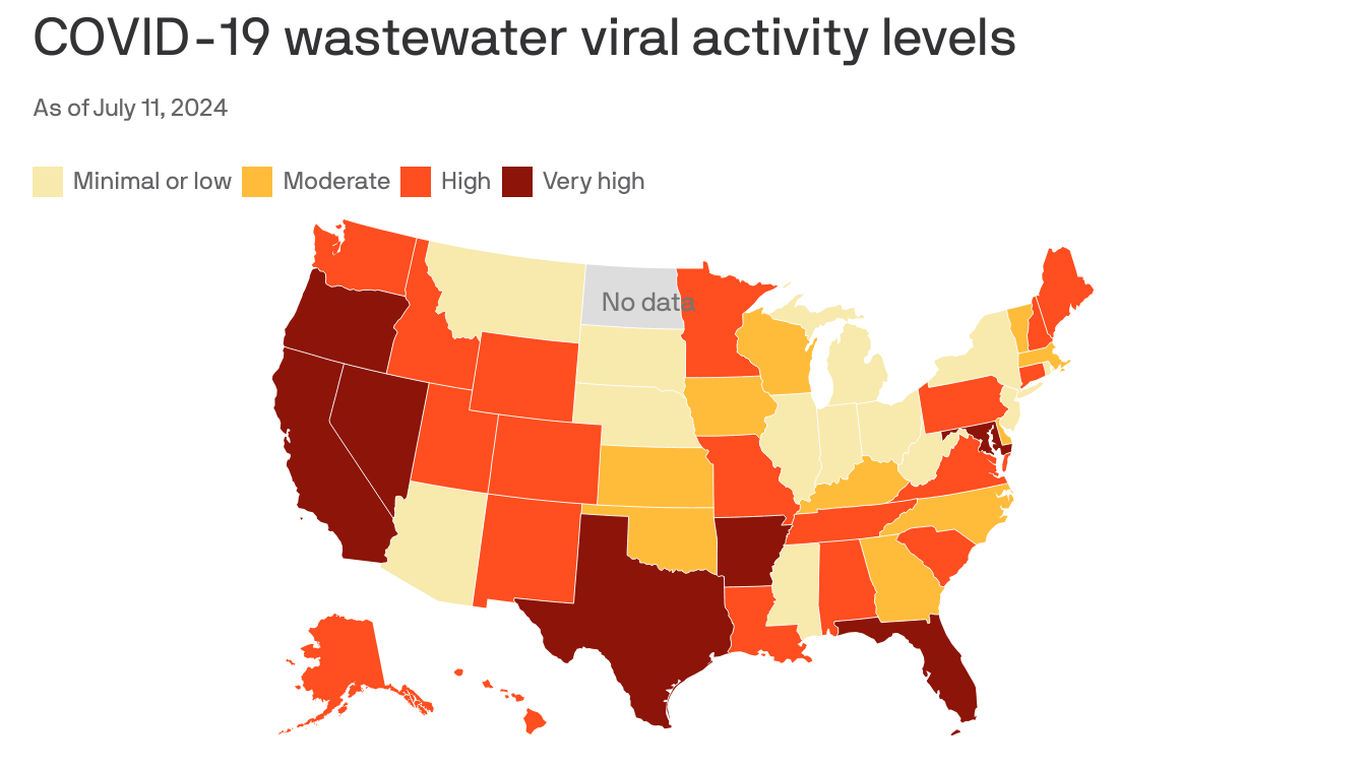
CDC Warns of COVID-19 Surge in 45 States: Prevalence of Contagious Variants and Rising Hospitalizations
Broke On: Monday, 15 July 2024
Persistent Immune Cell Activity and SARS-CoV-2 RNA Traces in Organs of Individuals with Long COVID: Insights from UCSF and CellSight Technologies Studies
Broke On: Tuesday, 09 July 2024
CDC Warns of Rising Covid-19 Levels in US: New KP.2 and KP.3 Variants Account for Over Half of Infections
Broke On: Friday, 28 June 2024
USDA Announces Compensation for Dairy Farmers Affected by Bird Flu Outbreak
Broke On: Friday, 28 June 2024
Unprecedented Surge in Dengue Cases: Over 9.7 Million Reported in Americas Region in 2024
Broke On: Tuesday, 25 June 2024