Title: Alaska's Top-Heavy Glaciers Approaching an Irreversible Tipping Point
Introduction: Alaska, home to some of the largest icefields on the planet, is experiencing accelerated glacier melt. This melting contributes significantly to sea-level rise and could have far-reaching consequences for coastal areas worldwide. In this article, we will explore recent findings regarding the melting of Alaska's Juneau icefield and its potential implications.
Facts:
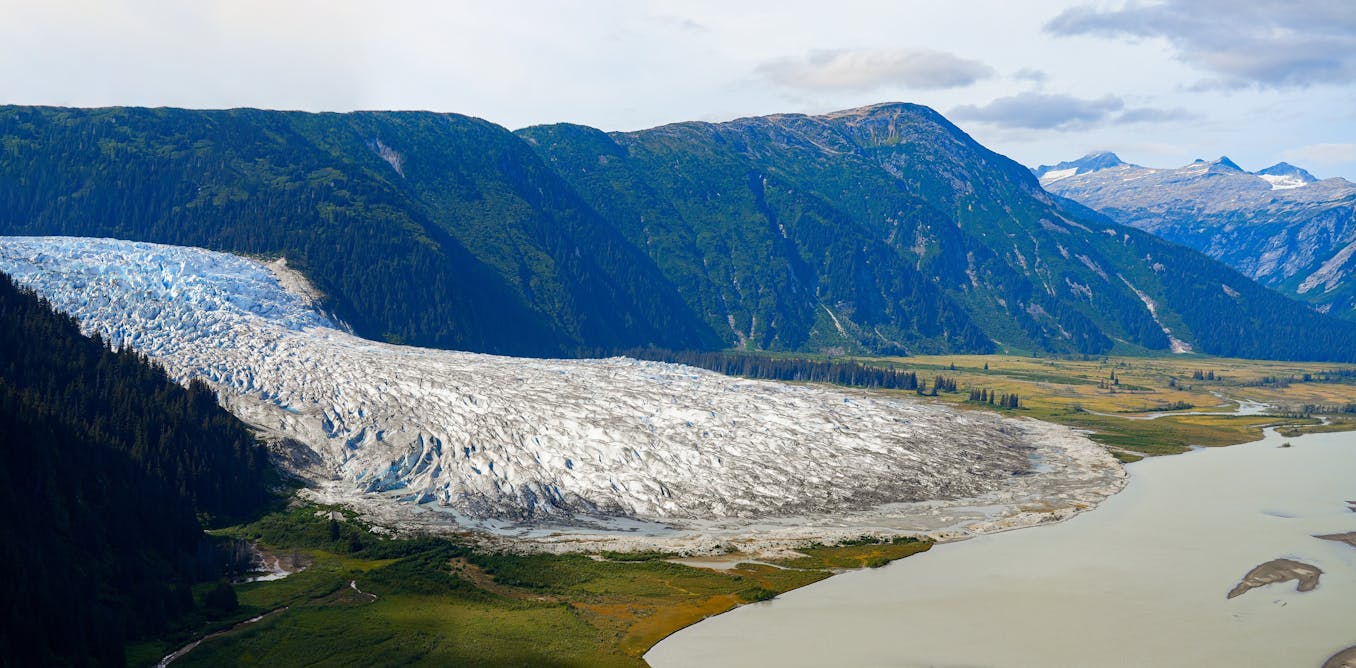
- Alaska's Juneau icefield, a massive area of interconnected glaciers near Juneau, is losing snow at an alarming rate – 4.6 times faster than in the 1980s.
- One larger glacier, Antler glacier, has completely melted away.
- Between 2005 and 2019, 64 glaciers in the Juneau icefield disappeared compared to only four between 1948 and 2005.
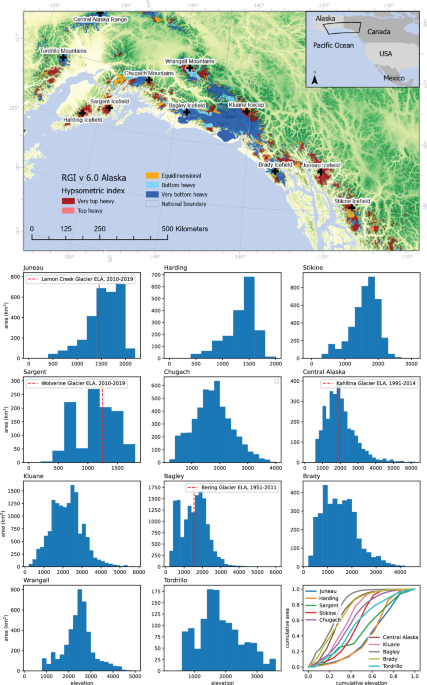
Background: Alaskan icefields are particularly vulnerable to accelerated melt due to their hypsometrically top-heavy or plateau structure and low-slope accumulation areas. The melting trend is driven by rising temperatures, which have been linked to human-induced climate change.
Impact: The loss of glacier ice in Alaska will contribute significantly to global sea level rise. Model projections indicate that land ice will drive 25cm (11, 40cm at 5th, 95th percentiles) sea-level rise by 2100 AD. Of this, approximately one quarter will come from Alaskan glaciers alone.
Bias: It is important to note that the mainstream media may present a biased perspective on this issue due to their tendency to focus on sensational headlines and dramatic imagery. It is crucial for readers to remain skeptical and seek out diverse sources of information in order to form a well-informed opinion.
Conclusion: The melting of Alaska's Juneau icefield is accelerating at an alarming rate, with potentially far-reaching consequences for global sea level rise. It is essential that we remain informed about this issue and take steps to mitigate the causes of climate change in order to preserve our planet's precious natural resources.