Nature Magazine
Nature Magazine is a multidisciplinary scientific journal founded in 1869. It is published by Springer Nature and covers various scientific disciplines including physics, chemistry, biology, earth sciences, and more. The magazine's mission is to publish high-quality research articles that contribute to the advancement of knowledge in science. Nature Magazine has a strong reputation for publishing groundbreaking research and attracting top scientists from around the world.
78%
The Daily's Verdict
This news site has a mixed reputation for journalistic standards. It is advisable to fact-check, scrutinize for bias, and check for conflicts of interest before relying on its reporting.
Bias
100%
Examples:
No current examples available.
Conflicts of Interest
100%
Examples:
No current examples available.
Contradictions
5%
Examples:
- Minimal adaptation may be needed for SARS-CoV-2 transmission among deer following initial human-to-animal transmission events.
- SARS-CoV-2 has caused over 771 million human cases and over six million deaths worldwide.
Deceptions
30%
Examples:
- Despite promising data that have sped treatments towards approval, researchers still don't fully understand the mechanism that underlies their therapeutic effects.
- These findings, published in Nature on 17 July1, could offer insights into why the compound might have a therapeutic effect on some neurological conditions.
Recent Articles

Six Common Wildlife Species in the US Test Positive for SARS-CoV-2: Study
Broke On: Monday, 29 July 2024
Newly Discovered Chimpanzee Recordings Suggest Complex Vocal Capabilities, Challenging Previous Assumptions About Speech Evolution
Broke On: Thursday, 25 July 2024
New Insights into Alzheimer's Disease: Reelin, Neurofibrillary Tangles, and Emerging Biomarkers
Broke On: Monday, 29 July 2024
Urgent Action Needed: Preventing Liver Cancer Deaths in South-East Asia through Viral Hepatitis B and C Treatment and Prevention
Broke On: Monday, 29 July 2024
Space Travel and Human Health: Unraveling the Effects of Microgravity and Radiation on the Cornea and Immune System
Broke On: Tuesday, 23 July 2024
Revolutionizing Cancer Detection: AI Outperforms Human Doctors with 84% Accuracy in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Broke On: Monday, 22 July 2024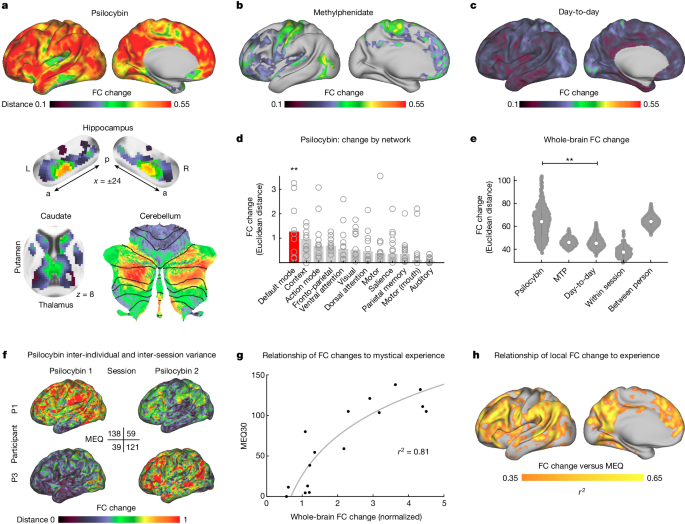
New Study Reveals Psilocybin's Impact on Brain, Temporarily Resets Neurons and Disrupts Communication
Broke On: Wednesday, 17 July 2024
New Study Reveals Psilocybin's Impact on Brain, Temporarily Resets Neurons and Disrupts Communication
Broke On: Wednesday, 17 July 2024
Newly Discovered Lunar Cave System: Potential Shelter for Future Astronauts and Insight into Lunar Volcanism
Broke On: Wednesday, 17 July 2024