Title: Spaceflight and its Impact on Human Health: A Comprehensive Analysis
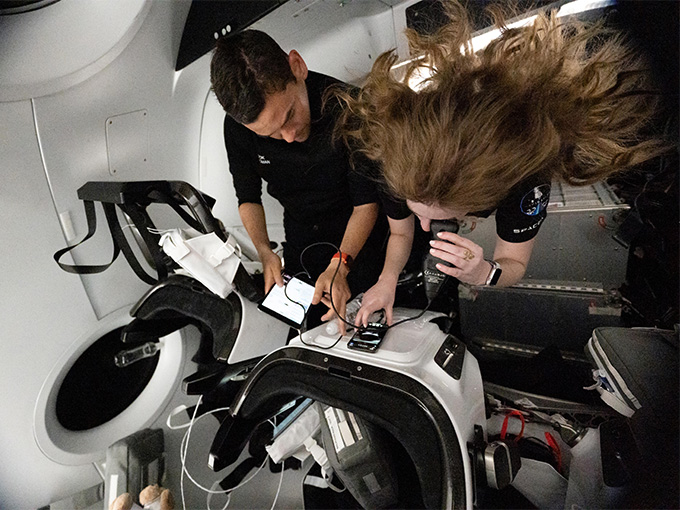
Space travel, whether for professional astronauts or space tourists, brings about significant changes to the human body. These alterations can range from mental shifts to physical transformations, collectively known as the Overview Effect.
The cornea is a critical component of the eye that has been identified as a concern due to its sensitivity to environmental changes in microgravity and direct exposure to space and spacecraft environments. Studies on mice following spaceflight have shown evidence of corneal edema, epithelial thickening, and signs of DNA damage and increased apoptosis.
Spaceflight exposes astronauts to various environmental stressors, including microgravity and radiation. While the individual impacts of these factors on the immune system have been extensively studied, a comprehensive review on their combined effects is lacking. It is essential to understand synergistic, additive, and antagonistic interactions between microgravity and radiation on immune function as observed during spaceflight-analog studies such as rodent hindlimb unloading and cell culture rotating wall vessel models.
Professional astronauts undergo rigorous health tests before embarking on missions, but private space travelers do not. The SOMA project, the largest published database on aerospace medicine and space biology, provides valuable information regarding the health risks associated with commercial space tourism.
Space tourists could face out-of-this-world health risks such as bone loss, cancer risk, vision impairment, brain tissue drops, and immunity weakening. These conditions are a result of prolonged exposure to microgravity and radiation in space.
NASA's Artemis missions to the Moon and Mars will have varying immunological risks from microgravity and radiation exposure. Understanding these risks is crucial for optimizing human corneal health, minimizing risks, and ensuring mission performance.
Ed White was the first American to walk in space on June 3, 1965 during the Gemini IV mission. Since then, humans have faced numerous challenges while adapting to outer space conditions. These challenges include lower gravity and higher radiation levels with no emergency room access.