Title: Spaceflight and Its Impact on the Human Body: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Findings
Lead: Space travel, whether for tourism or long-term missions to Mars, poses unique challenges to human health. Recent studies have shed light on the effects of spaceflight on various aspects of the human body. In this article, we delve into these findings and explore what they mean for future space exploration.
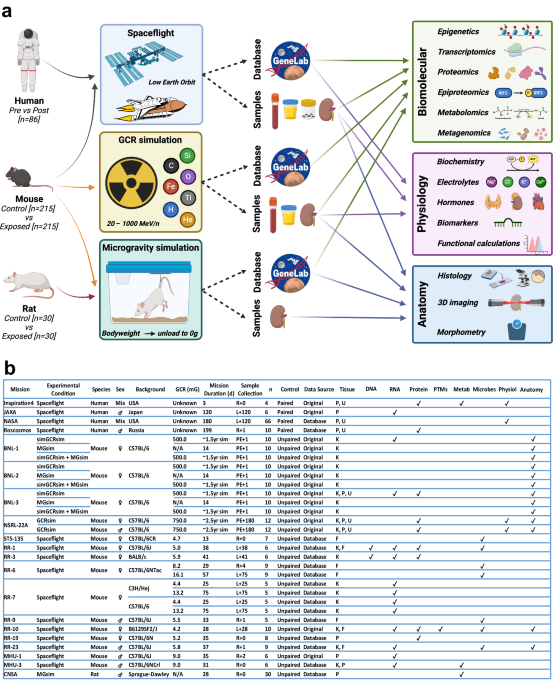
Paragraph 1: Spaceflight and Cellular Changes Four civilians who participated in the SpaceX Inspiration4 mission experienced changes similar to astronauts after their short trip to space. Researchers analyzed samples of their blood, saliva, skin, and more upon their return home. The studies revealed wide-ranging shifts in cells and changes to the immune system for all four passengers.
Paragraph 2: Recovery from Spaceflight Most of these cellular shifts stabilized within a few months after the tourists returned to Earth. However, researchers noted that short-term spaceflight did not pose significant health risks. The findings provide valuable insights into how people adapt to weightlessness and space radiation.
Paragraph 3: Gender Differences in Spaceflight Response Female crew members seemed to recover faster from the spaceflight than their male counterparts. This observation could have implications for future long-term missions, as women may be better suited for extended stays in space.
Paragraph 4: Telomere Length and DNA Aging Another study revealed that telomeres, protective caps on chromosomes that shorten with age, got longer for the Inspiration4 crew members while they were in space. This finding suggests that the space environment may have anti-aging effects on human DNA.
Paragraph 5: The Future of Space Travel and Research As commercial space travel continues to grow and national space agencies focus on sending humans to the moon and Mars, it is crucial to understand the health implications of these journeys. New insights from studies like these could help researchers develop countermeasures against the negative effects of space travel, extend human health-span, and improve our overall understanding of how humans adapt to extreme environments.
Conclusion: Space travel presents unique challenges for human health. Recent research has provided valuable insights into the cellular changes that occur during spaceflight and the potential implications for future missions. As we continue to explore the cosmos, it is essential to prioritize scientific research and understanding of these effects to ensure the safety and well-being of astronauts.


