EurekAlert
EurekAlert is a platform for academic institutions and organizations to share their research findings. The site covers a wide range of topics including health, environment, technology, and more. The articles are well-written and easy to understand with a focus on the key findings of the research. While there may be occasional contradictions within the articles, there is no apparent editorial bias or conflicts of interest.
100%
The Daily's Verdict
This news site is known for its high journalistic standards. It strives to maintain neutrality and transparency in its reporting, and avoids conflicts of interest. It has a reputation for accuracy and rarely gets contradicted on major discrepancies in its reporting.
Bias
100%
Examples:
- EurekAlert appears to provide a platform for various academic institutions and organizations to share their research findings without any apparent editorial bias.
Conflicts of Interest
100%
Examples:
- There are no apparent conflicts of interest reported in any of the articles.
Contradictions
85%
Examples:
- In one article, it is mentioned that WASP-39b, the studied exoplanet, has a diameter 1.3 times greater than Jupiter and is tidally locked to its parent star. However, it is also stated that the planet's eternal morning side is likely cloudier than its eternal evening due to differences in temperature and atmospheric circulation.
Deceptions
100%
Examples:
- No deceptive practices were found in the articles.
Recent Articles

Unprecedented Volcanic Eruption Cooled Earth in 2022, Challenging Global Warming Assumptions
Broke On: Saturday, 15 January 2022Blocking Inflammatory Protein IL-11 Extends Healthy Lifespan of Mice by 25%: New Study Reveals
Broke On: Wednesday, 17 July 2024
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Reveals Distinct Morning and Evening Atmospheres on Exoplanet WASP-39b: A Tidally Locked World with Extreme Temperature Differences
Broke On: Tuesday, 16 July 2024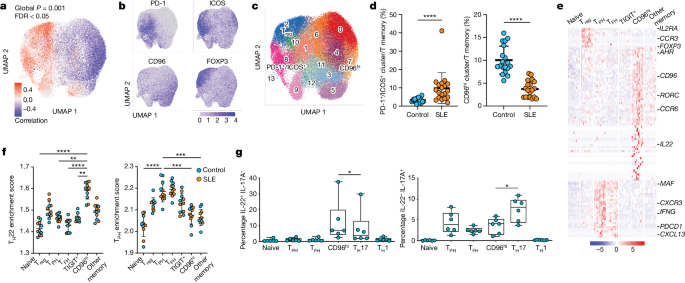
New Insights into the Role of AHR in Regulating T Cell CXCL13 Production and Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Broke On: Wednesday, 10 July 2024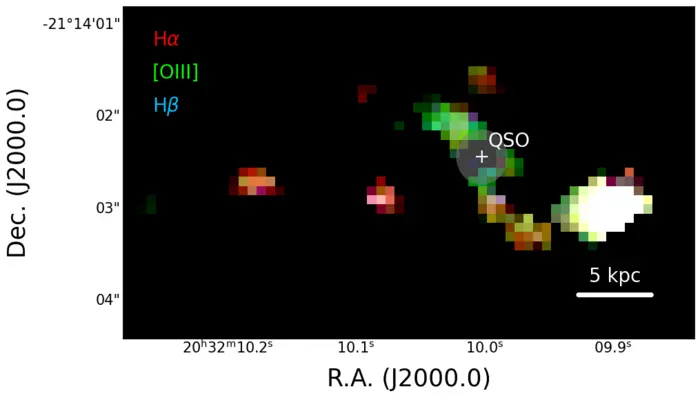
New Discovery: Quasar Merges with Two Galaxies, Revealing Early Galaxy Formation and Black Hole Growth
Broke On: Friday, 05 July 2024
New Studies Question the Assumption that Minimally Processed Foods are Healthier than Ultra-Processed Ones
Broke On: Sunday, 30 June 2024
New Study: Unnatural Greenhouse Gases on Exoplanets Could Be Signs of Alien Civilizations Terraforming Worlds
Broke On: Wednesday, 26 June 2024