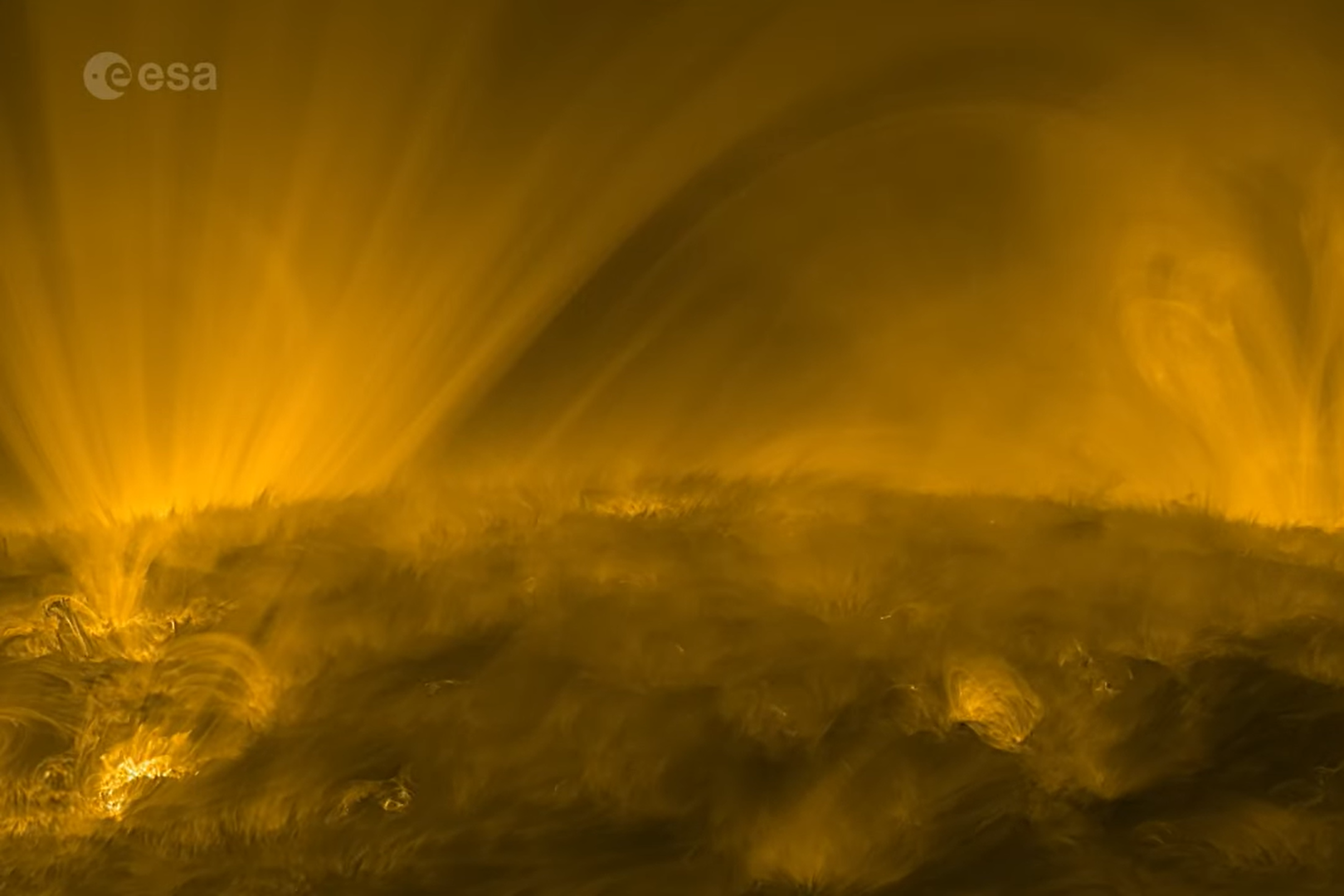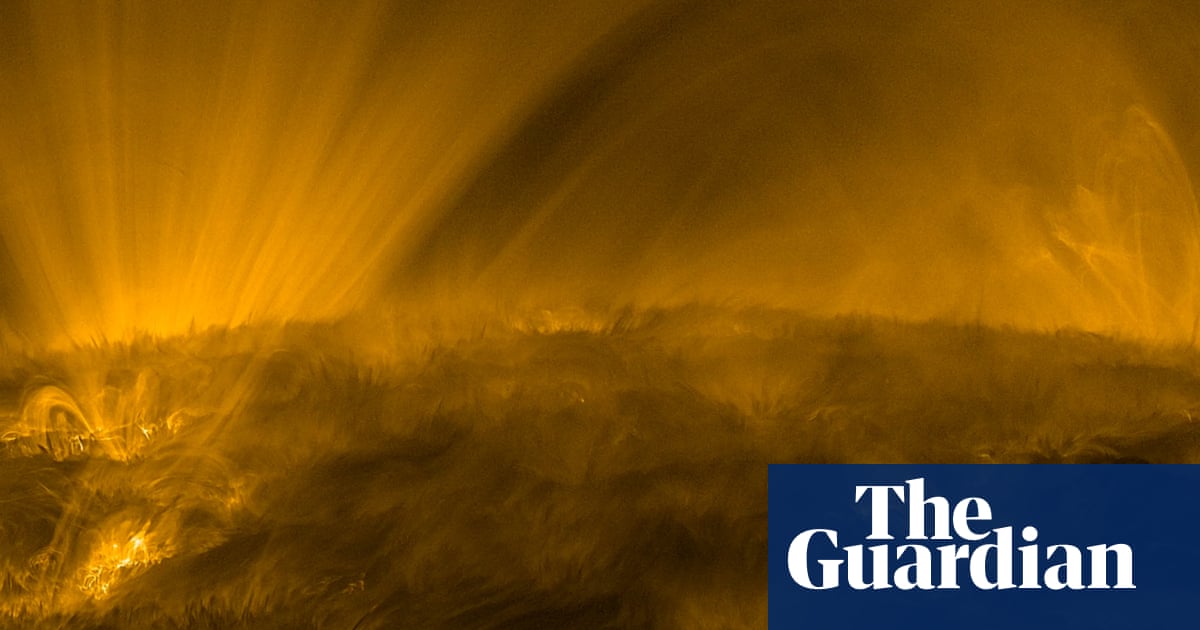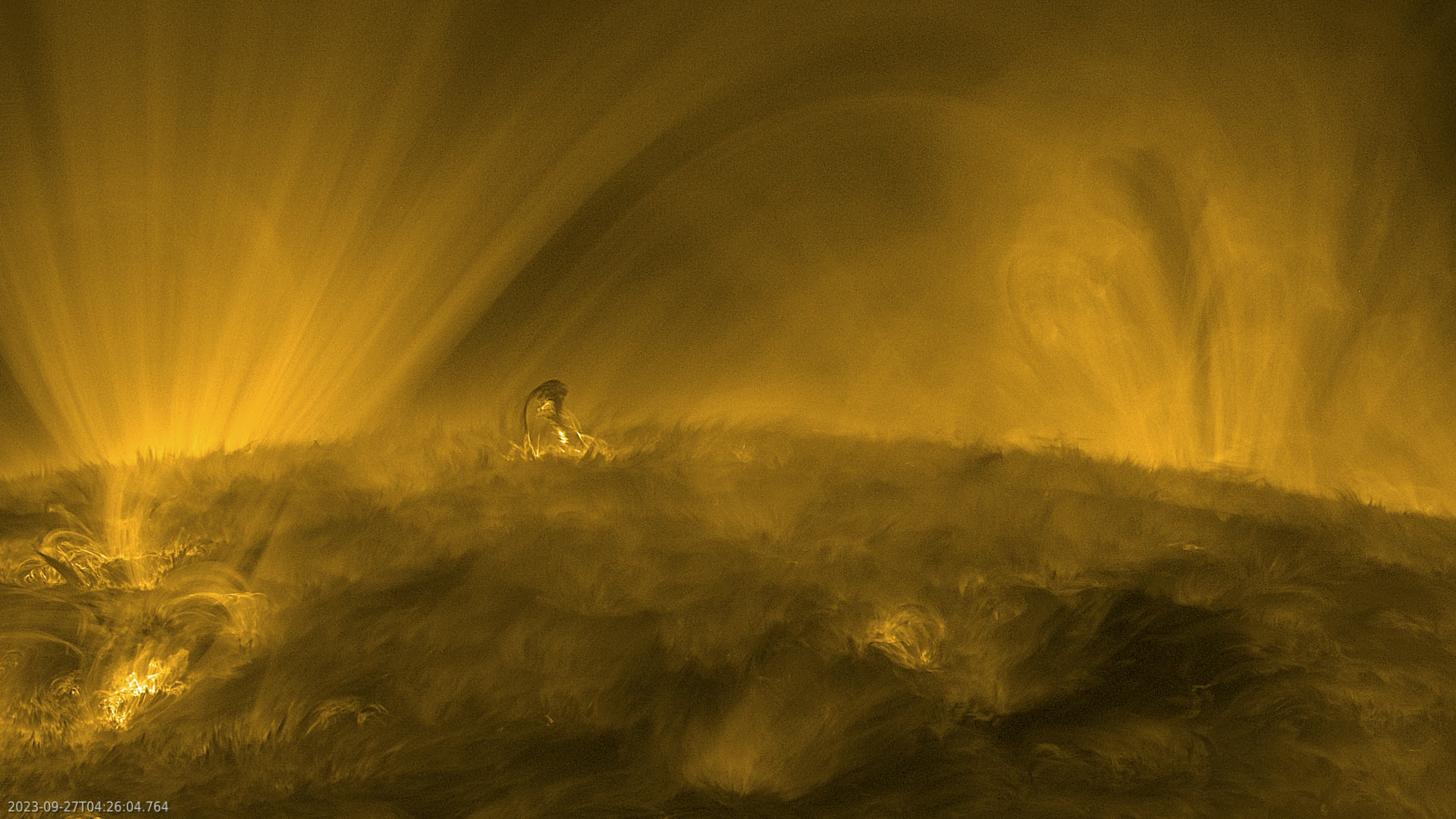
On September 27, 2023, the European Space Agency's (ESA) Solar Orbiter and NASA's Parker Solar Probe collaborated to observe the solar wind source region. The Extreme Ultraviolet Imager (EUI) on Solar Orbiter captured a video of the Sun at roughly a third of Earth's distance from it, revealing intriguing features such as coronal moss, spicules, and coronal rain on its surface. These structures provide valuable insights into the Sun's complex dynamics.
Coronal moss appears as delicate, lace-like patterns around large coronal loops that are too hot or too tenuous to be seen with the chosen instrument settings. It usually forms around the base of these loops and spans two atmospheric layers: the chromosphere and corona. Spicules are tall spires of gas seen along the solar horizon, reaching up to about 10,000 km from its chromosphere.
Coronal rain is cooler than other surface features and made of high-density clumps of plasma that fall back towards the Sun due to gravity. It looks dark against the bright background of large coronal loops (around one million degrees).
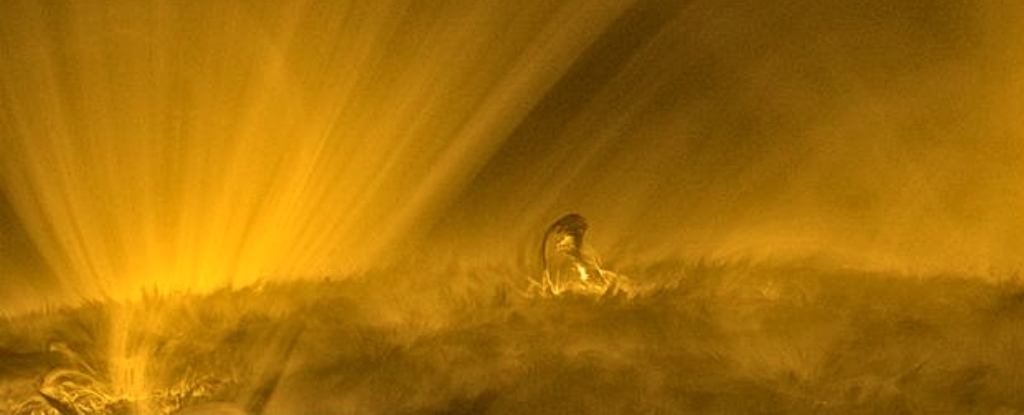
On September 27, 2023, Solar Orbiter recorded a small eruption in the center of its field view at about 0:20 seconds in the video. Despite being called 'small,' this eruption was actually bigger than Earth.
Two missions, Solar Orbiter and Parker Solar Probe, teamed up to observe the solar wind source region on that day. While Solar Orbiter observed the source region with its remote-sensing instruments, Parker measured particles and the magnetic field in the Sun's corona and solar wind.
The video was recorded using EUI on September 27, 2023, when Solar Orbiter was about a third of Earth's distance from the Sun. At that time, NASA's Parker Solar Probe skimmed just 7.26 million km from the solar surface.
The video reveals intriguing features such as coronal moss, spicules, and coronal rain on the Sun's surface. Coronal moss appears as delicate, lace-like patterns around large coronal loops that are too hot or too tenuous to be seen with the chosen instrument settings. Spicules are tall spires of gas seen along the solar horizon that reach up to about 10,000 km from its chromosphere. Coronal rain is cooler than other surface features and made of high-density clumps of plasma that fall back towards the Sun due to gravity.
At about 20 seconds into the video, a small eruption occurs in the center of the field view. Despite being called 'small,' this eruption is actually bigger than Earth.
The collaboration between Solar Orbiter and Parker Solar Probe provided valuable insights into the solar wind source region on September 27, 2023. The data collected by both missions will contribute to a better understanding of the Sun's complex dynamics.



